Nonlinear parametric model for Granger causality of time series
Paper and Code
Feb 07, 2006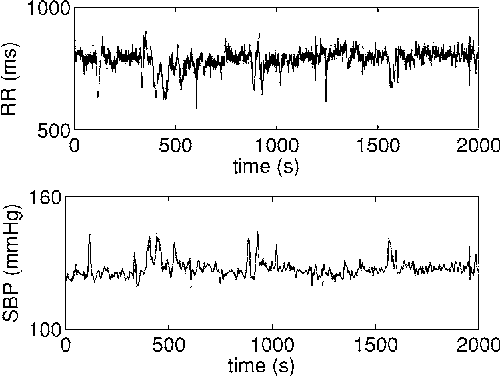
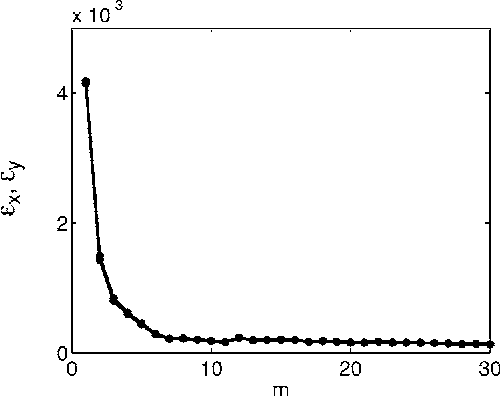

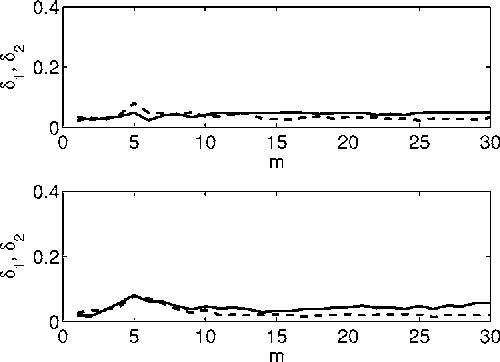
We generalize a previously proposed approach for nonlinear Granger causality of time series, based on radial basis function. The proposed model is not constrained to be additive in variables from the two time series and can approximate any function of these variables, still being suitable to evaluate causality. Usefulness of this measure of causality is shown in a physiological example and in the study of the feed-back loop in a model of excitatory and inhibitory neurons.
* 4 pages 5 figures
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge