Neural Distributed Compressor Discovers Binning
Paper and Code
Oct 25, 2023
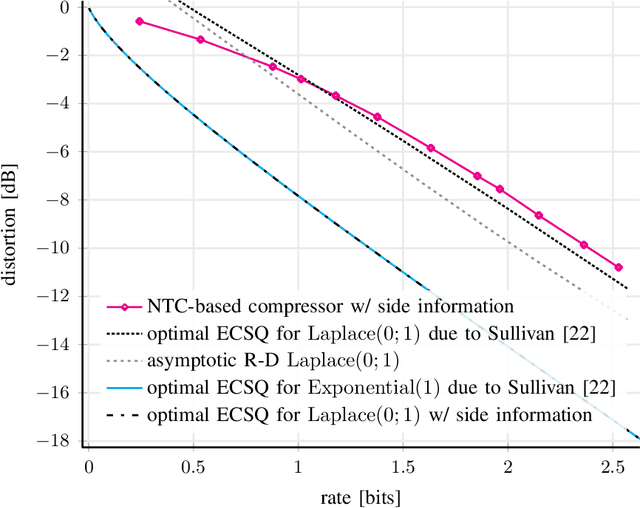
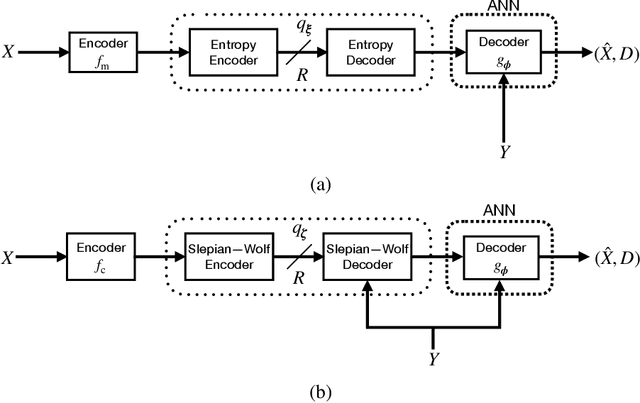
We consider lossy compression of an information source when the decoder has lossless access to a correlated one. This setup, also known as the Wyner-Ziv problem, is a special case of distributed source coding. To this day, practical approaches for the Wyner-Ziv problem have neither been fully developed nor heavily investigated. We propose a data-driven method based on machine learning that leverages the universal function approximation capability of artificial neural networks. We find that our neural network-based compression scheme, based on variational vector quantization, recovers some principles of the optimum theoretical solution of the Wyner-Ziv setup, such as binning in the source space as well as optimal combination of the quantization index and side information, for exemplary sources. These behaviors emerge although no structure exploiting knowledge of the source distributions was imposed. Binning is a widely used tool in information theoretic proofs and methods, and to our knowledge, this is the first time it has been explicitly observed to emerge from data-driven learning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge