Network Parameter Learning Using Nonlinear Transforms, Local Representation Goals and Local Propagation Constraints
Paper and Code
Jan 31, 2019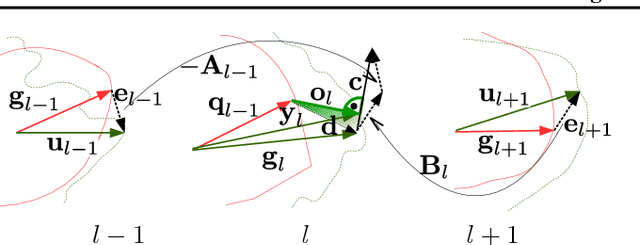
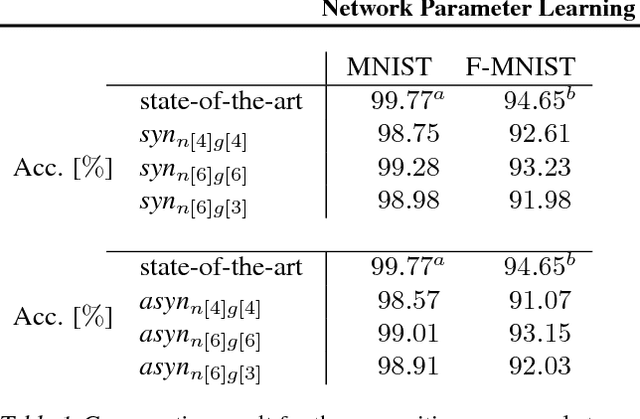
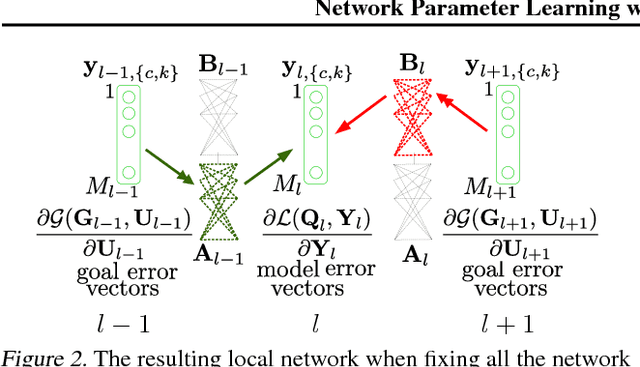

In this paper, we introduce a novel concept for learning of the parameters in a neural network. Our idea is grounded on modeling a learning problem that addresses a trade-off between (i) satisfying local objectives at each node and (ii) achieving desired data propagation through the network under (iii) local propagation constraints. We consider two types of nonlinear transforms which describe the network representations. One of the nonlinear transforms serves as activation function. The other one enables a locally adjusted, deviation corrective components to be included in the update of the network weights in order to enable attaining target specific representations at the last network node. Our learning principle not only provides insight into the understanding and the interpretation of the learning dynamics, but it offers theoretical guarantees over decoupled and parallel parameter estimation strategy that enables learning in synchronous and asynchronous mode. Numerical experiments validate the potential of our approach on image recognition task. The preliminary results show advantages in comparison to the state-of-the-art methods, w.r.t. the learning time and the network size while having competitive recognition accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge