Nested Grassmanns for Dimensionality Reduction
Paper and Code
Oct 27, 2020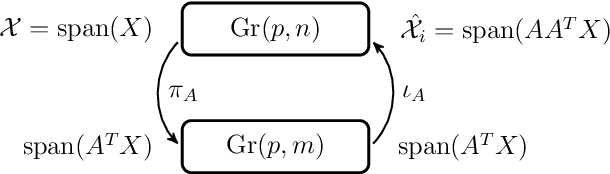
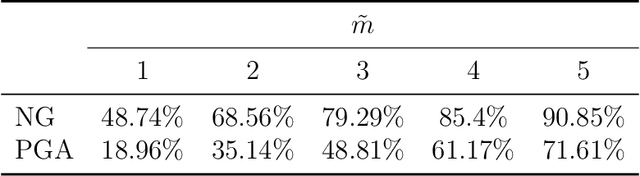
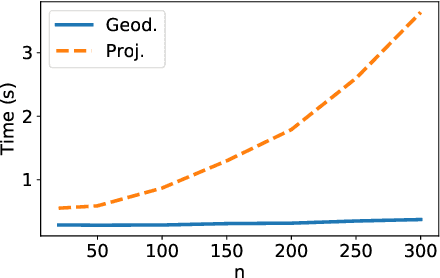
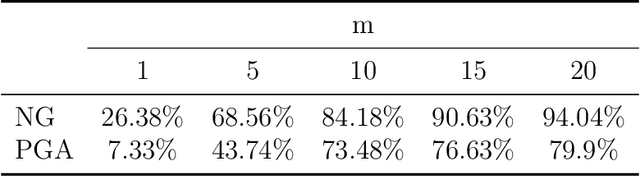
Grassmann manifolds have been widely used to represent the geometry of feature spaces in a variety of problems in computer vision including but not limited to face recognition, action recognition, subspace clustering and motion segmentation. For these problems, the features usually lie in a very high-dimensional Grassmann manifold and hence an appropriate dimensionality reduction technique is called for in order to curtail the computational burden. To this end, the Principal Geodesic Analysis (PGA), a nonlinear extension of the well known principal component analysis, is applicable as a general tool to many Riemannian manifolds. In this paper, we propose a novel dimensionality reduction framework suited for Grassmann manifolds by utilizing the geometry of the manifold. Specifically, we project points in a Grassmann manifold to an embedded lower dimensional Grassmann manifold. A salient feature of our method is that it leads to higher expressed variance compared to PGA which we demonstrate via synthetic and real data experiments.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge