Multitask Learning for Blackmarket Tweet Detection
Paper and Code
Jul 09, 2019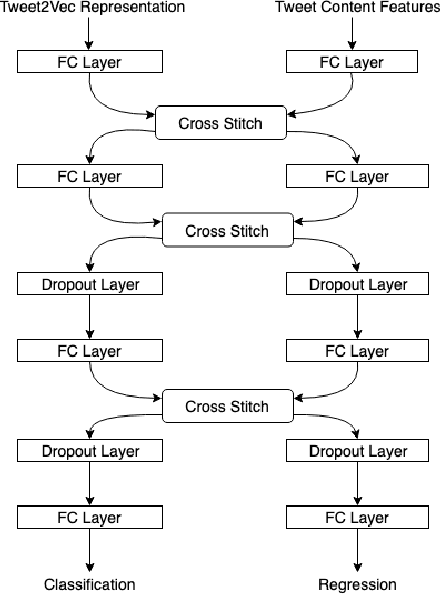
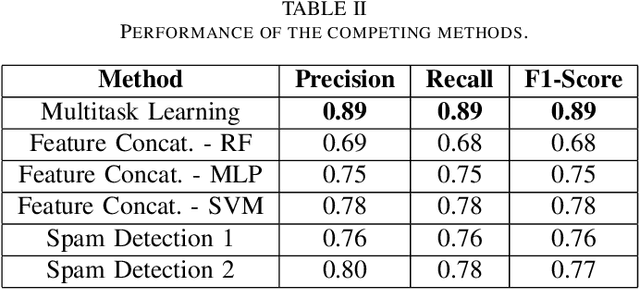
Online social media platforms have made the world more connected than ever before, thereby making it easier for everyone to spread their content across a wide variety of audiences. Twitter is one such popular platform where people publish tweets to spread their messages to everyone. Twitter allows users to Retweet other users' tweets in order to broadcast it to their network. The more retweets a particular tweet gets, the faster it spreads. This creates incentives for people to obtain artificial growth in the reach of their tweets by using certain blackmarket services to gain inorganic appraisals for their content. In this paper, we attempt to detect such tweets that have been posted on these blackmarket services in order to gain artificially boosted retweets. We use a multitask learning framework to leverage soft parameter sharing between a classification and a regression based task on separate inputs. This allows us to effectively detect tweets that have been posted to these blackmarket services, achieving an F1-score of 0.89 when classifying tweets as blackmarket or genuine.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge