Multiple Sclerosis Lesions Segmentation using Attention-Based CNNs in FLAIR Images
Paper and Code
Jan 05, 2022
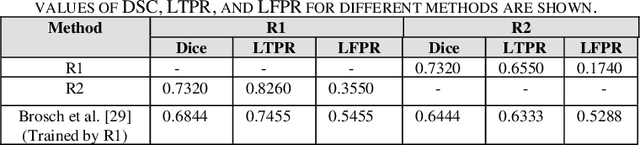

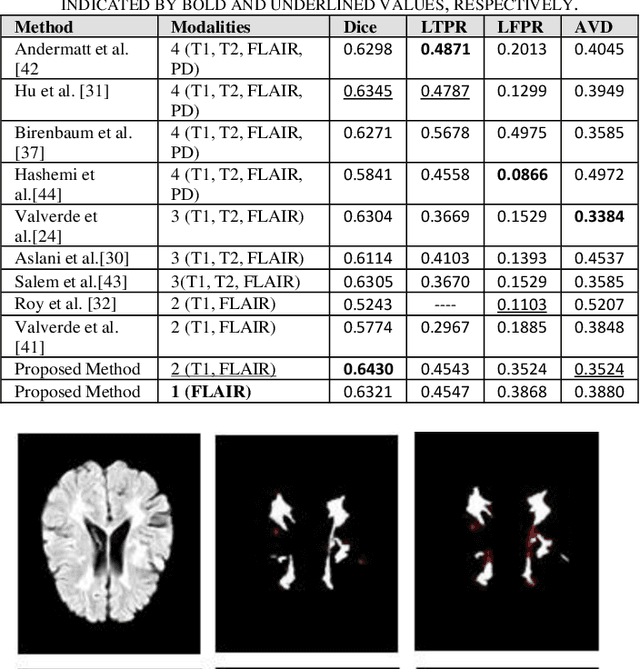
Objective: Multiple Sclerosis (MS) is an autoimmune, and demyelinating disease that leads to lesions in the central nervous system. This disease can be tracked and diagnosed using Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI). Up to now a multitude of multimodality automatic biomedical approaches is used to segment lesions which are not beneficial for patients in terms of cost, time, and usability. The authors of the present paper propose a method employing just one modality (FLAIR image) to segment MS lesions accurately. Methods: A patch-based Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) is designed, inspired by 3D-ResNet and spatial-channel attention module, to segment MS lesions. The proposed method consists of three stages: (1) the contrast-limited adaptive histogram equalization (CLAHE) is applied to the original images and concatenated to the extracted edges in order to create 4D images; (2) the patches of size 80 * 80 * 80 * 2 are randomly selected from the 4D images; and (3) the extracted patches are passed into an attention-based CNN which is used to segment the lesions. Finally, the proposed method was compared to previous studies of the same dataset. Results: The current study evaluates the model, with a test set of ISIB challenge data. Experimental results illustrate that the proposed approach significantly surpasses existing methods in terms of Dice similarity and Absolute Volume Difference while the proposed method use just one modality (FLAIR) to segment the lesions. Conclusions: The authors have introduced an automated approach to segment the lesions which is based on, at most, two modalities as an input. The proposed architecture is composed of convolution, deconvolution, and an SCA-VoxRes module as an attention module. The results show, the proposed method outperforms well compare to other methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge