Multiple Intelligent Reflecting Surface aided Multi-user Weighted Sum-Rate Maximization using Manifold Optimization
Paper and Code
Sep 29, 2021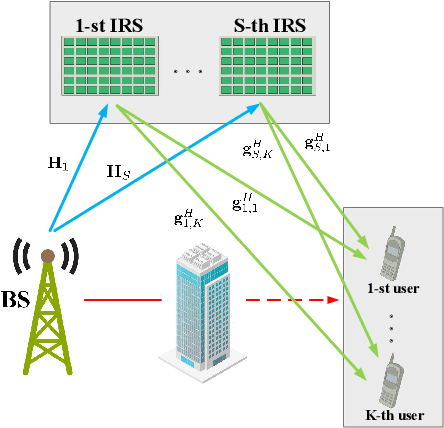

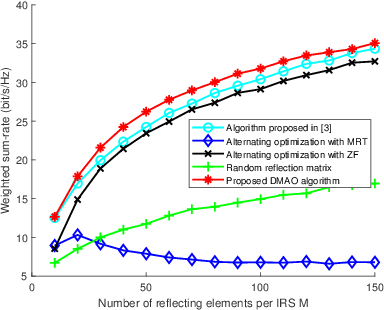
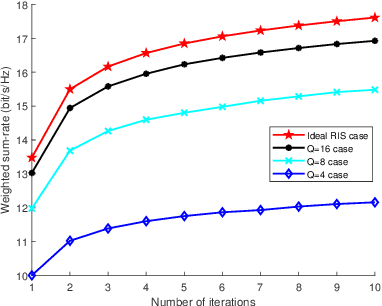
Intelligent reflecting surface (IRS) are able to amend radio propagation condition tasks on account of its functional properties in phase shift optimizing. In fact, there exists geometry manifold in the base-station (BS) beamforming matrix and IRS reflection vector. Therefore, we propose a novel double manifold alternating optimization (DMAO) algorithm which makes use of differential geometry theory to improve optimization performance. First, we develop a multi-IRS multi-user system model to maximize the weighted sum-rate, which may lead to the non-convexity in our optimization procedure. Then in order to allocate an optimized coefficients to each BS antenna and IRS reflecting element, we present the beamforming matrix and reflection vector using complex sphere manifold and complex oblique manifold, respectively, which integrates the inner geometry structure and the constrains. By an innovative alternative iteration method, the system gradually converges an optimized stable state, which is associating with the maximized sum-rate. Furthermore, we quantize the IRS reflection coefficient considering the practical constrains. Experimental results demonstrated that our approach significantly outperforms the conventional methods in terms of weighted sum-rate.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge