Multi-Vector Models with Textual Guidance for Fine-Grained Scientific Document Similarity
Paper and Code
Nov 16, 2021
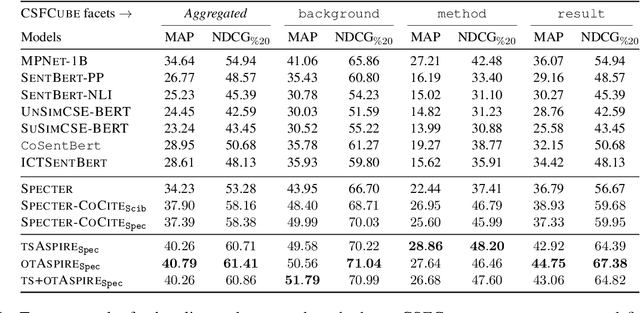

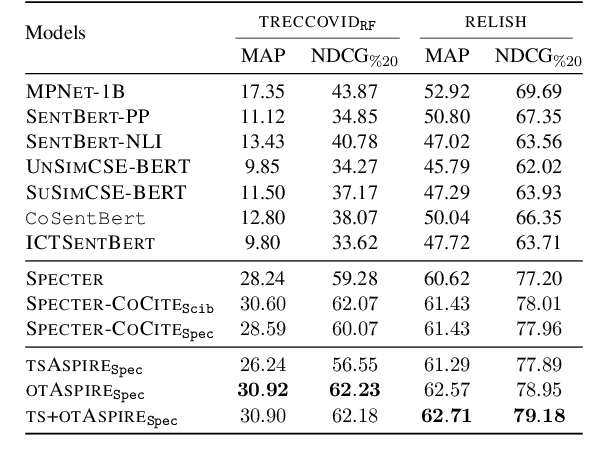
We present Aspire, a new scientific document similarity model based on matching fine-grained aspects. Our model is trained using co-citation contexts that describe related paper aspects as a novel form of textual supervision. We use multi-vector document representations, recently explored in settings with short query texts but under-explored in the challenging document-document setting. We present a fast method that involves matching only single sentence pairs, and a method that makes sparse multiple matches with optimal transport. Our model improves performance on document similarity tasks across four datasets. Moreover, our fast single-match method achieves competitive results, opening up the possibility of applying fine-grained document similarity models to large-scale scientific corpora.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge