Multi-User SR-LDPC Codes via Coded Demixing with Applications to Cell-Free Systems
Paper and Code
Feb 10, 2024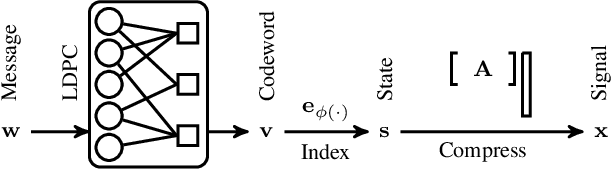
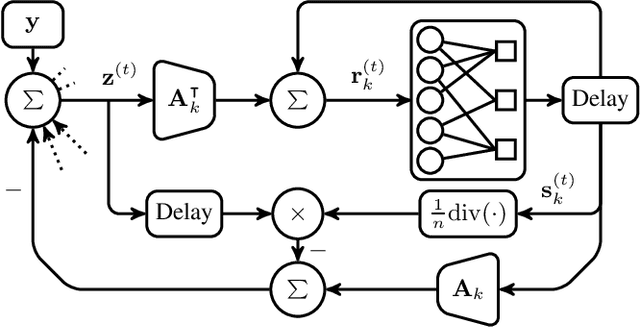


Novel sparse regression LDPC (SR-LDPC) codes exhibit excellent performance over additive white Gaussian noise (AWGN) channels in part due to their natural provision of shaping gains. Though SR-LDPC-like codes have been considered within the context of single-user error correction and massive random access, they are yet to be examined as candidates for coordinated multi-user communication scenarios. This article explores this gap in the literature and demonstrates that SR-LDPC codes, when combined with coded demixing techniques, offer a new framework for efficient non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) in the context of coordinated multi-user communication channels. The ensuing communication scheme is referred to as MU-SR-LDPC coding. Empirical evidence suggests that, for a fixed SNR, MU-SR-LDPC coding can achieve a target bit error rate (BER) at a higher sum rate than orthogonal multiple access (OMA) techniques such as time division multiple access (TDMA) and frequency division multiple access (FDMA). Importantly, MU-SR-LDPC codes enable a pragmatic solution path for user-centric cell-free communication systems with (local) joint decoding. Results are supported by numerical simulations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge