Multi-resource allocation for federated settings: A non-homogeneous Markov chain model
Paper and Code
Apr 26, 2021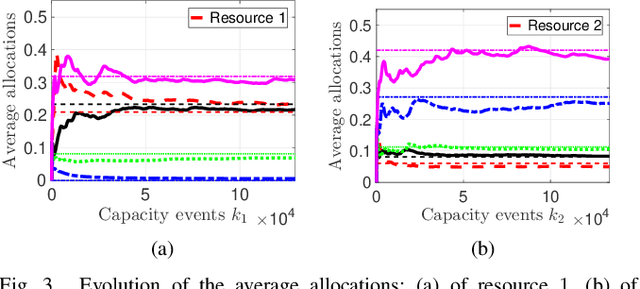
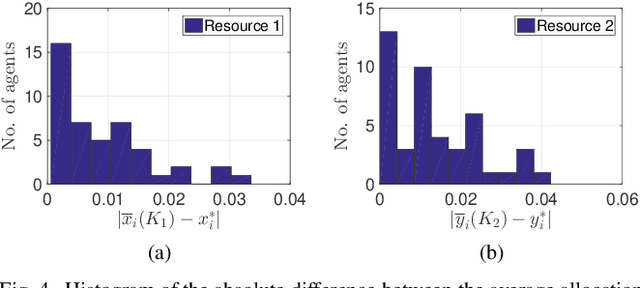
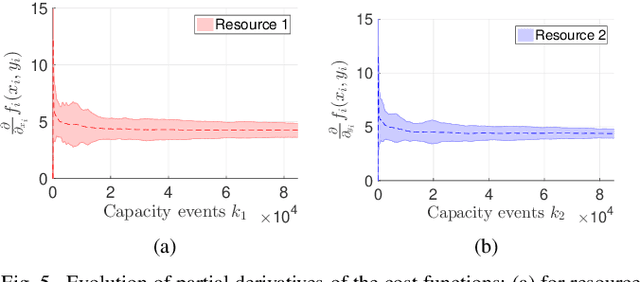
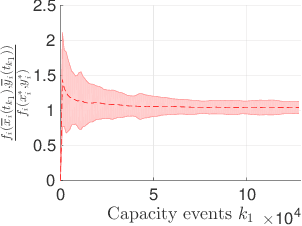
In a federated setting, agents coordinate with a central agent or a server to solve an optimization problem in which agents do not share their information with each other. Wirth and his co-authors, in a recent paper, describe how the basic additive-increase multiplicative-decrease (AIMD) algorithm can be modified in a straightforward manner to solve a class of optimization problems for federated settings for a single shared resource with no inter-agent communication. The AIMD algorithm is one of the most successful distributed resource allocation algorithms currently deployed in practice. It is best known as the backbone of the Internet and is also widely explored in other application areas. We extend the single-resource algorithm to multiple heterogeneous shared resources that emerge in smart cities, sharing economy, and many other applications. Our main results show the convergence of the average allocations to the optimal values. We model the system as a non-homogeneous Markov chain with place-dependent probabilities. Furthermore, simulation results are presented to demonstrate the efficacy of the algorithms and to highlight the main features of our analysis.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge