MTStereo 2.0: improved accuracy of stereo depth estimation withMax-trees
Paper and Code
Jun 27, 2020

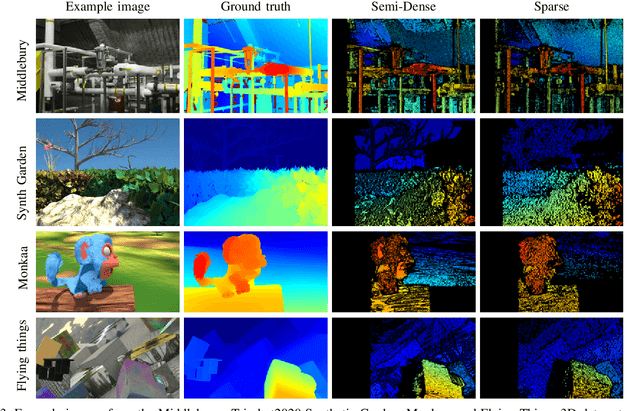

Efficient yet accurate extraction of depth from stereo image pairs is required by systems with low power resources, such as robotics and embedded systems. State-of-the-art stereo matching methods based on convolutional neural networks require intensive computations on GPUs and are difficult to deploy on embedded systems. In this paper, we propose a stereo matching method, called MTStereo 2.0, for limited-resource systems that require efficient and accurate depth estimation. It is based on a Max-tree hierarchical representation of image pairs, which we use to identify matching regions along image scan-lines. The method includes a cost function that considers similarity of region contextual information based on the Max-trees and a disparity border preserving cost aggregation approach. MTStereo 2.0 improves on its predecessor MTStereo 1.0 as it a) deploys a more robust cost function, b) performs more thorough detection of incorrect matches, c) computes disparity maps with pixel-level rather than node-level precision. MTStereo provides accurate sparse and semi-dense depth estimation and does not require intensive GPU computations like methods based on CNNs. Thus it can run on embedded and robotics devices with low-power requirements. We tested the proposed approach on several benchmark data sets, namely KITTI 2015, Driving, FlyingThings3D, Middlebury 2014, Monkaa and the TrimBot2020 garden data sets, and achieved competitive accuracy and efficiency. The code is available at https://github.com/rbrandt1/MaxTreeS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge