MPruner: Optimizing Neural Network Size with CKA-Based Mutual Information Pruning
Paper and Code
Aug 24, 2024
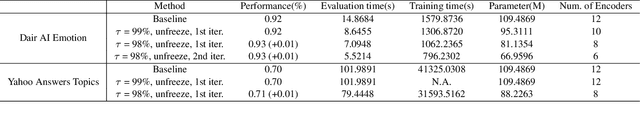
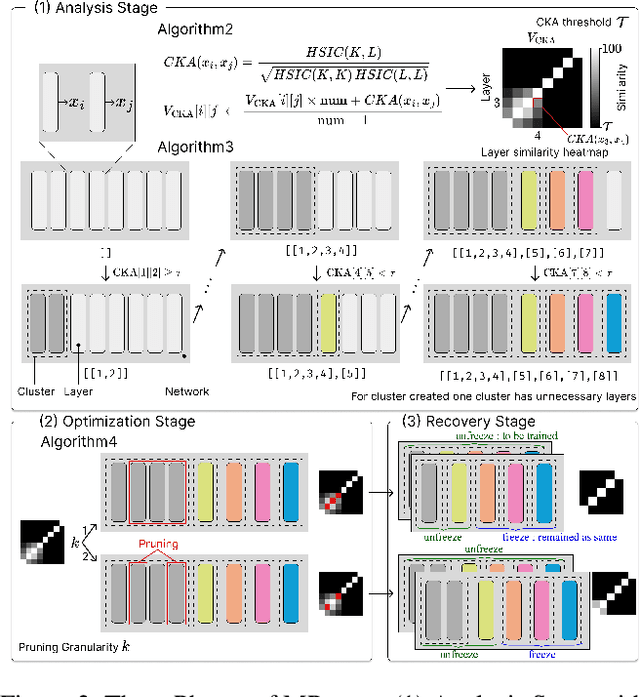
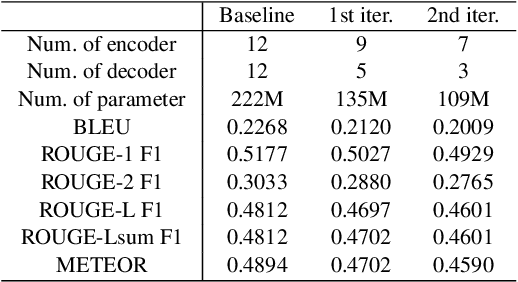
Determining the optimal size of a neural network is critical, as it directly impacts runtime performance and memory usage. Pruning is a well-established model compression technique that reduces the size of neural networks while mathematically guaranteeing accuracy preservation. However, many recent pruning methods overlook the global contributions of individual model components, making it difficult to ensure that a pruned model meets the desired dataset and performance requirements. To address these challenges, we developed a new pruning algorithm, MPruner, that leverages mutual information through vector similarity. MPruner utilizes layer clustering with the Centered Kernel Alignment (CKA) similarity metric, allowing us to incorporate global information from the neural network for more precise and efficient layer-wise pruning. We evaluated MPruner across various architectures and configurations, demonstrating its versatility and providing practical guidelines. MPruner achieved up to a 50% reduction in parameters and memory usage for CNN and transformer-based models, with minimal to no loss in accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge