Motif-Centric Representation Learning for Symbolic Music
Paper and Code
Sep 19, 2023

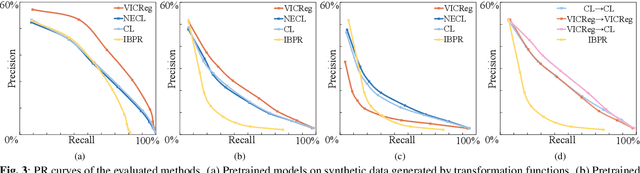
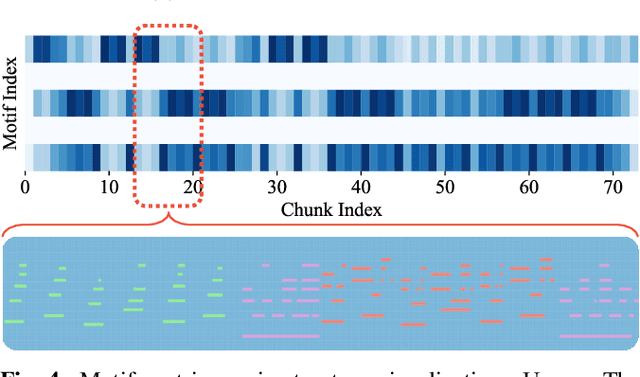
Music motif, as a conceptual building block of composition, is crucial for music structure analysis and automatic composition. While human listeners can identify motifs easily, existing computational models fall short in representing motifs and their developments. The reason is that the nature of motifs is implicit, and the diversity of motif variations extends beyond simple repetitions and modulations. In this study, we aim to learn the implicit relationship between motifs and their variations via representation learning, using the Siamese network architecture and a pretraining and fine-tuning pipeline. A regularization-based method, VICReg, is adopted for pretraining, while contrastive learning is used for fine-tuning. Experimental results on a retrieval-based task show that these two methods complement each other, yielding an improvement of 12.6% in the area under the precision-recall curve. Lastly, we visualize the acquired motif representations, offering an intuitive comprehension of the overall structure of a music piece. As far as we know, this work marks a noteworthy step forward in computational modeling of music motifs. We believe that this work lays the foundations for future applications of motifs in automatic music composition and music information retrieval.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge