Modeling speech recognition and synthesis simultaneously: Encoding and decoding lexical and sublexical semantic information into speech with no direct access to speech data
Paper and Code
Mar 29, 2022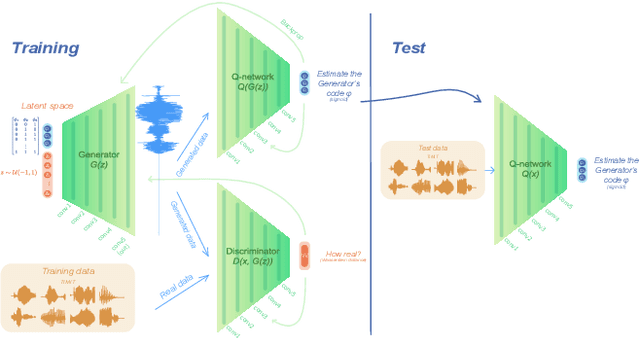
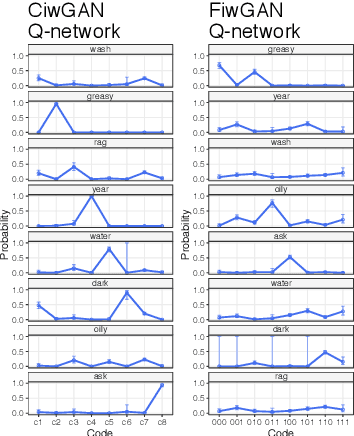
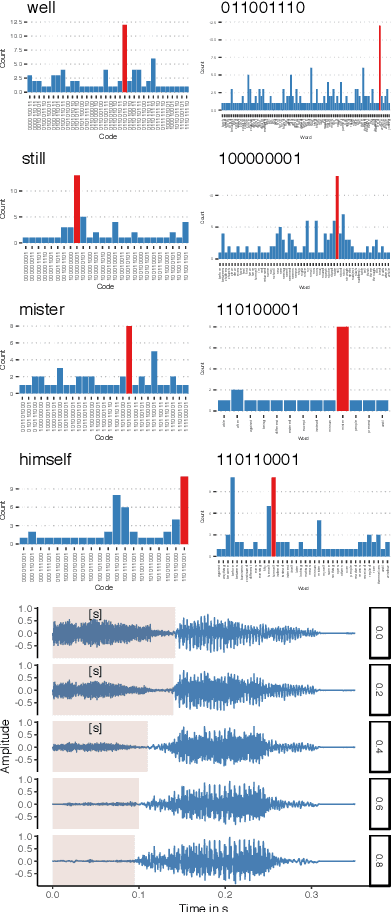
Human speakers encode information into raw speech which is then decoded by the listeners. This complex relationship between encoding (production) and decoding (perception) is often modeled separately. Here, we test how encoding and decoding of lexical semantic information can emerge automatically from raw speech in unsupervised generative deep convolutional networks that combine the production and perception principles of speech. We introduce, to our knowledge, the most challenging objective in unsupervised lexical learning: a network that must learn unique representations for lexical items with no direct access to training data. We train several models (ciwGAN and fiwGAN arXiv:2006.02951) and test how the networks classify acoustic lexical items in unobserved test data. Strong evidence in favor of lexical learning and a causal relationship between latent codes and meaningful sublexical units emerge. The architecture that combines the production and perception principles is thus able to learn to decode unique information from raw acoustic data without accessing real training data directly. We propose a technique to explore lexical (holistic) and sublexical (featural) learned representations in the classifier network. The results bear implications for unsupervised speech technology, as well as for unsupervised semantic modeling as language models increasingly bypass text and operate from raw acoustics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge