Modeling Score Distributions and Continuous Covariates: A Bayesian Approach
Paper and Code
Sep 21, 2020
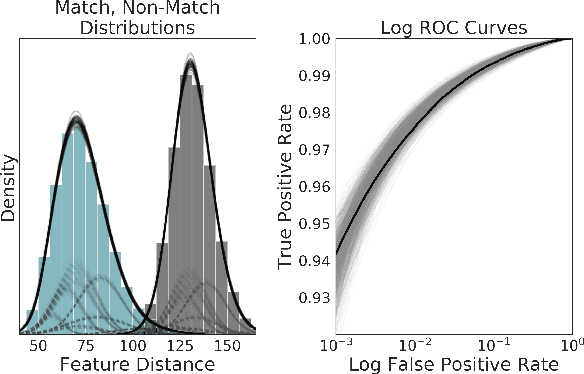
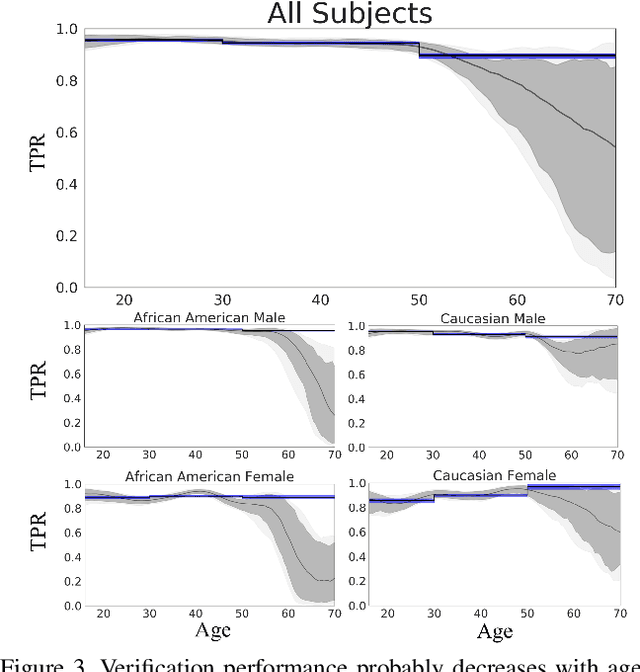
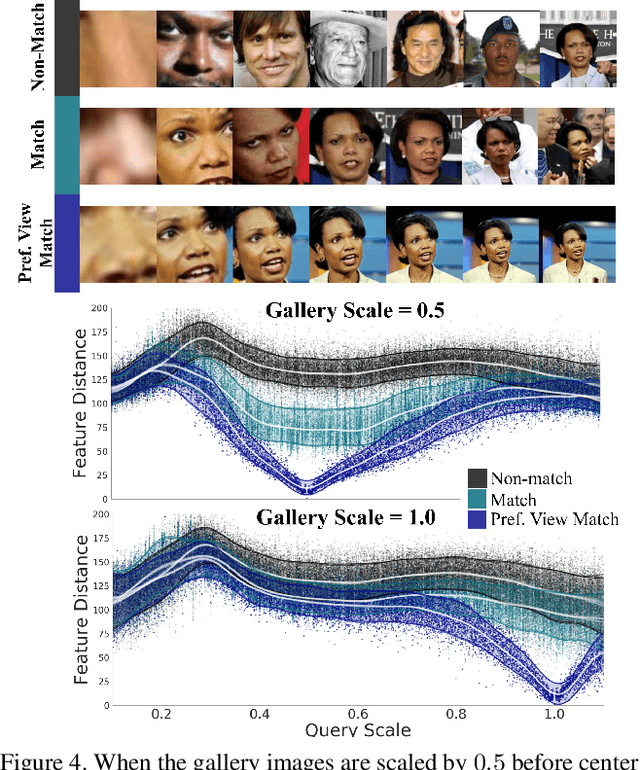
Computer Vision practitioners must thoroughly understand their model's performance, but conditional evaluation is complex and error-prone. In biometric verification, model performance over continuous covariates---real-number attributes of images that affect performance---is particularly challenging to study. We develop a generative model of the match and non-match score distributions over continuous covariates and perform inference with modern Bayesian methods. We use mixture models to capture arbitrary distributions and local basis functions to capture non-linear, multivariate trends. Three experiments demonstrate the accuracy and effectiveness of our approach. First, we study the relationship between age and face verification performance and find previous methods may overstate performance and confidence. Second, we study preprocessing for CNNs and find a highly non-linear, multivariate surface of model performance. Our method is accurate and data efficient when evaluated against previous synthetic methods. Third, we demonstrate the novel application of our method to pedestrian tracking and calculate variable thresholds and expected performance while controlling for multiple covariates.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge