Modeling Disagreement in Automatic Data Labelling for Semi-Supervised Learning in Clinical Natural Language Processing
Paper and Code
Jun 07, 2022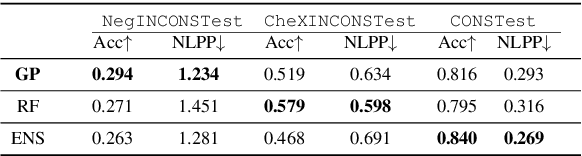
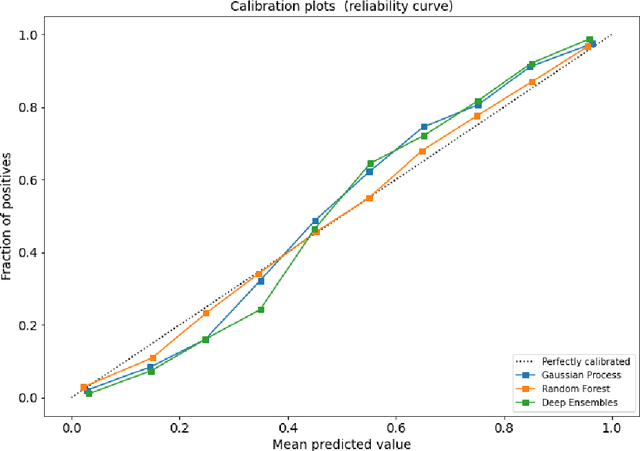
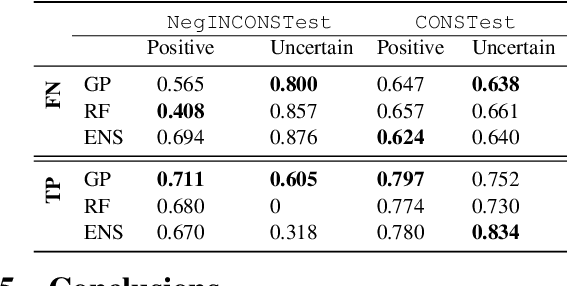
Computational models providing accurate estimates of their uncertainty are crucial for risk management associated with decision making in healthcare contexts. This is especially true since many state-of-the-art systems are trained using the data which has been labelled automatically (self-supervised mode) and tend to overfit. In this work, we investigate the quality of uncertainty estimates from a range of current state-of-the-art predictive models applied to the problem of observation detection in radiology reports. This problem remains understudied for Natural Language Processing in the healthcare domain. We demonstrate that Gaussian Processes (GPs) provide superior performance in quantifying the risks of 3 uncertainty labels based on the negative log predictive probability (NLPP) evaluation metric and mean maximum predicted confidence levels (MMPCL), whilst retaining strong predictive performance.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge