Model-based Offline Quantum Reinforcement Learning
Paper and Code
Apr 14, 2024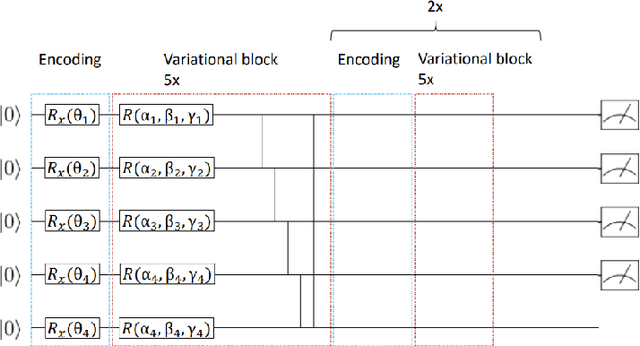
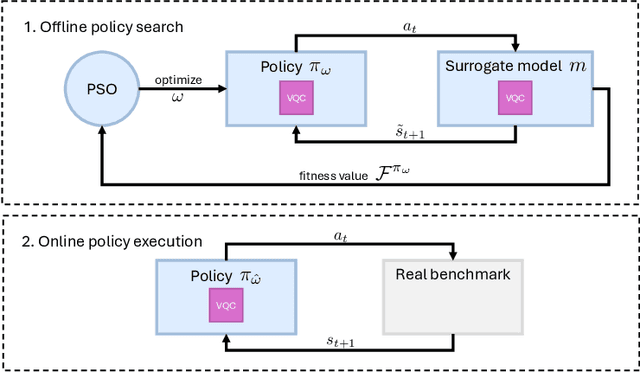
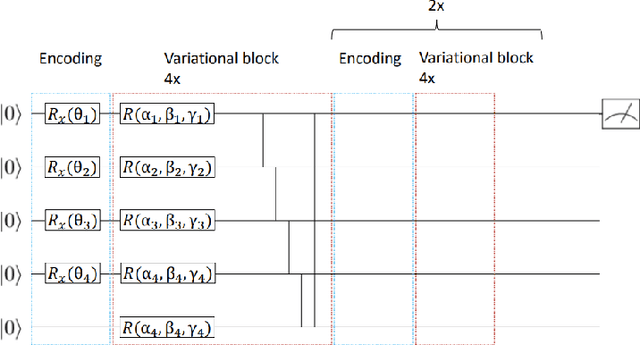
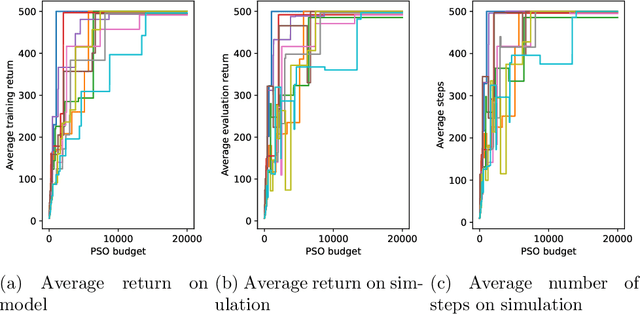
This paper presents the first algorithm for model-based offline quantum reinforcement learning and demonstrates its functionality on the cart-pole benchmark. The model and the policy to be optimized are each implemented as variational quantum circuits. The model is trained by gradient descent to fit a pre-recorded data set. The policy is optimized with a gradient-free optimization scheme using the return estimate given by the model as the fitness function. This model-based approach allows, in principle, full realization on a quantum computer during the optimization phase and gives hope that a quantum advantage can be achieved as soon as sufficiently powerful quantum computers are available.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge