Mode-Assisted Joint Training of Deep Boltzmann Machines
Paper and Code
Feb 17, 2021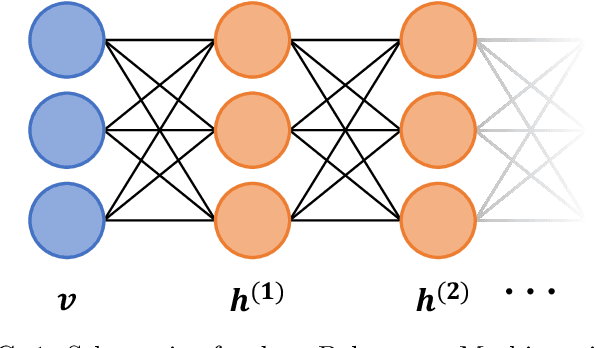
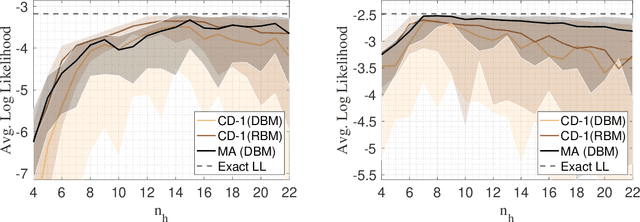
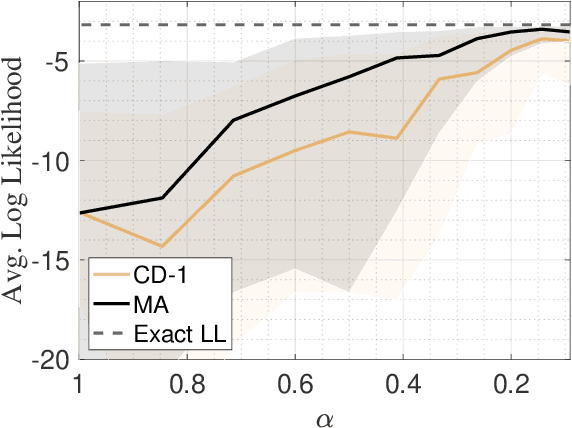
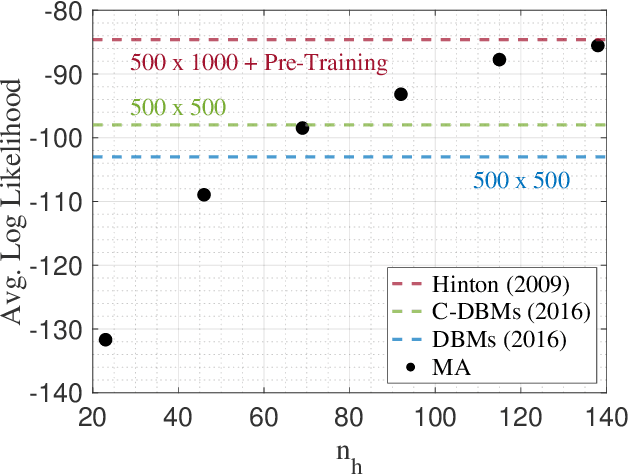
The deep extension of the restricted Boltzmann machine (RBM), known as the deep Boltzmann machine (DBM), is an expressive family of machine learning models which can serve as compact representations of complex probability distributions. However, jointly training DBMs in the unsupervised setting has proven to be a formidable task. A recent technique we have proposed, called mode-assisted training, has shown great success in improving the unsupervised training of RBMs. Here, we show that the performance gains of the mode-assisted training are even more dramatic for DBMs. In fact, DBMs jointly trained with the mode-assisted algorithm can represent the same data set with orders of magnitude lower number of total parameters compared to state-of-the-art training procedures and even with respect to RBMs, provided a fan-in network topology is also introduced. This substantial saving in number of parameters makes this training method very appealing also for hardware implementations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge