Microaneurysm Detection in Fundus Images Using a Two-step Convolutional Neural Networks
Paper and Code
Jul 08, 2018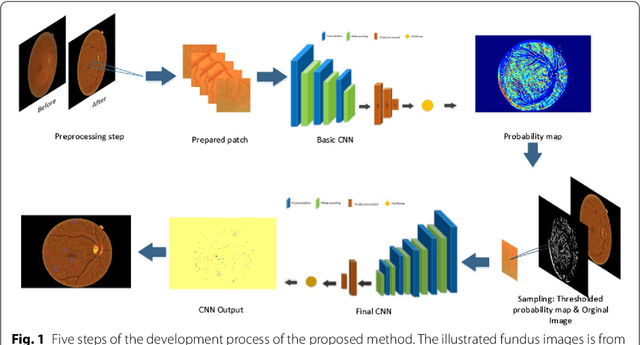
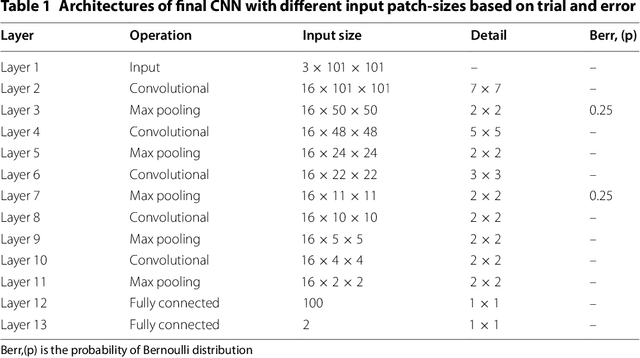
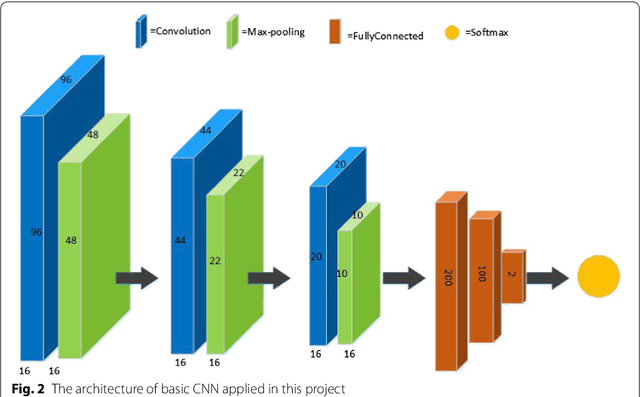
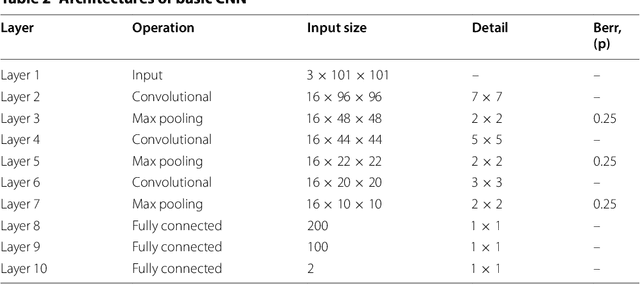
Diabetic Retinopathy (DR) is a prominent cause of blindness in the world. The early treatment of DR can be conducted from detection of microaneurysms (MAs) which appears as reddish spots in retinal images. An automated microaneurysm detection can be a helpful system for ophthalmologists. In this paper, deep learning, in particular convolutional neural network (CNN), is used as a powerful tool to efficiently detect MAs from fundus images. In our method a new technique is used to utilise a two-stage training process which results in an accurate detection, while decreasing computational complexity in comparison with previous works. To validate our proposed method, an experiment is conducted using Keras library to implement our proposed CNN on two standard publicly available datasets. Our results show a promising sensitivity value of about 0.8 at the average number of false positive per image greater than 6 which is a competitive value with the state-of-the-art approaches.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge