Metric Learning and Adaptive Boundary for Out-of-Domain Detection
Paper and Code
Apr 22, 2022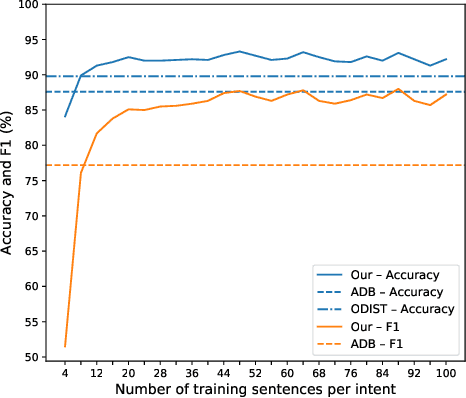
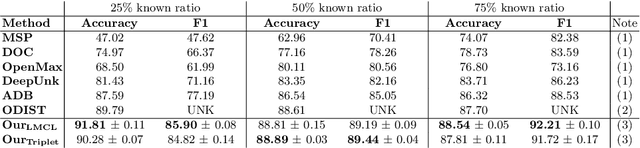
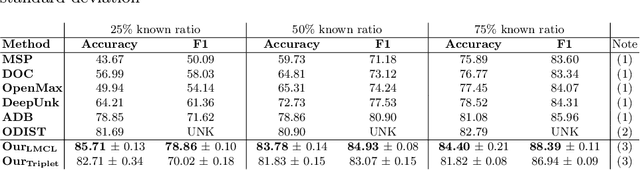
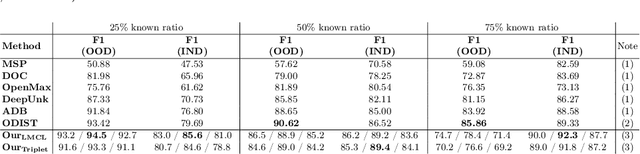
Conversational agents are usually designed for closed-world environments. Unfortunately, users can behave unexpectedly. Based on the open-world environment, we often encounter the situation that the training and test data are sampled from different distributions. Then, data from different distributions are called out-of-domain (OOD). A robust conversational agent needs to react to these OOD utterances adequately. Thus, the importance of robust OOD detection is emphasized. Unfortunately, collecting OOD data is a challenging task. We have designed an OOD detection algorithm independent of OOD data that outperforms a wide range of current state-of-the-art algorithms on publicly available datasets. Our algorithm is based on a simple but efficient approach of combining metric learning with adaptive decision boundary. Furthermore, compared to other algorithms, we have found that our proposed algorithm has significantly improved OOD performance in a scenario with a lower number of classes while preserving the accuracy for in-domain (IND) classes.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge