Metric-based Regularization and Temporal Ensemble for Multi-task Learning using Heterogeneous Unsupervised Tasks
Paper and Code
Aug 29, 2019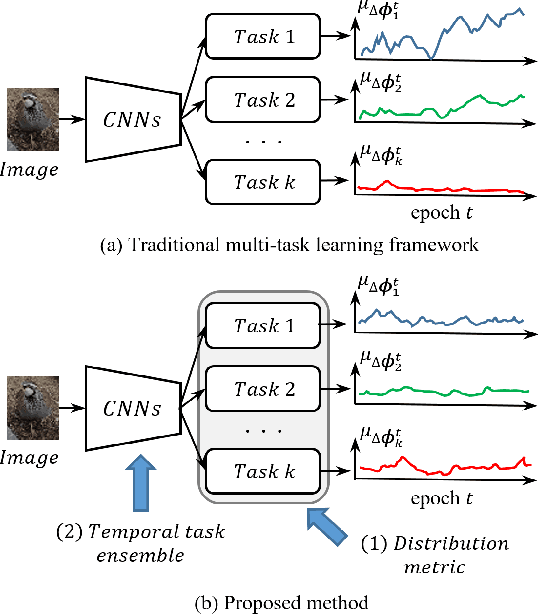
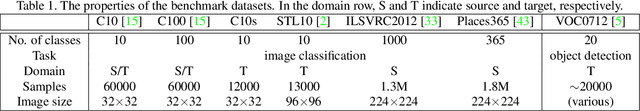
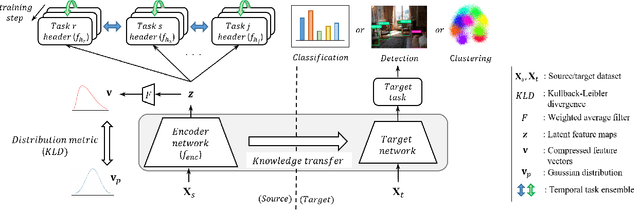
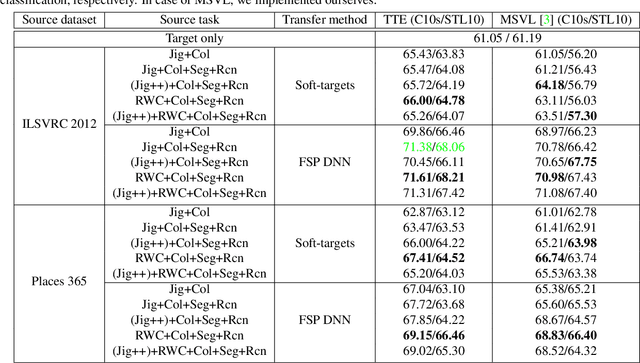
One of the ways to improve the performance of a target task is to learn the transfer of abundant knowledge of a pre-trained network. However, learning of the pre-trained network requires high computation capability and large-scale labeled dataset. To mitigate the burden of large-scale labeling, learning in un/self-supervised manner can be a solution. In addition, using unsupervised multi-task learning, a generalized feature representation can be learned. However, unsupervised multi-task learning can be biased to a specific task. To overcome this problem, we propose the metric-based regularization term and temporal task ensemble (TTE) for multi-task learning. Since these two techniques prevent the entire network from learning in a state deviated to a specific task, it is possible to learn a generalized feature representation that appropriately reflects the characteristics of each task without biasing. Experimental results for three target tasks such as classification, object detection and embedding clustering prove that the TTE-based multi-task framework is more effective than the state-of-the-art (SOTA) method in improving the performance of a target task.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge