Meta-heuristic for non-homogeneous peak density spaces and implementation on 2 real-world parameter learning/tuning applications
Paper and Code
Jun 13, 2019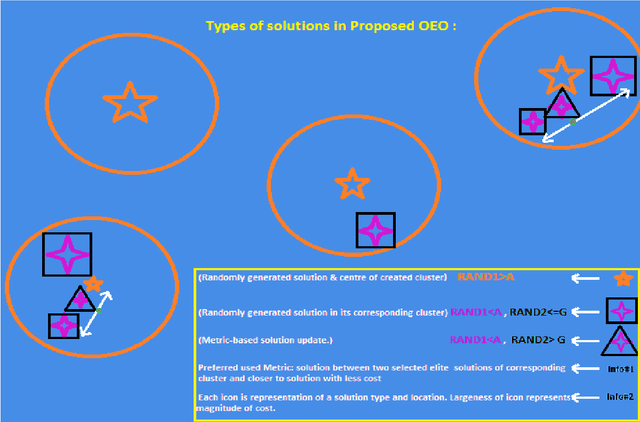
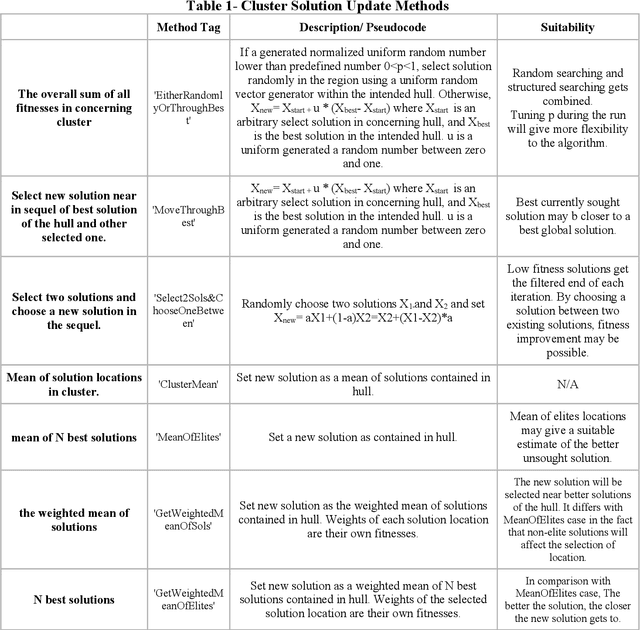
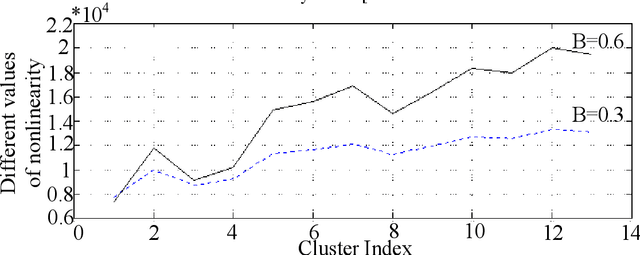
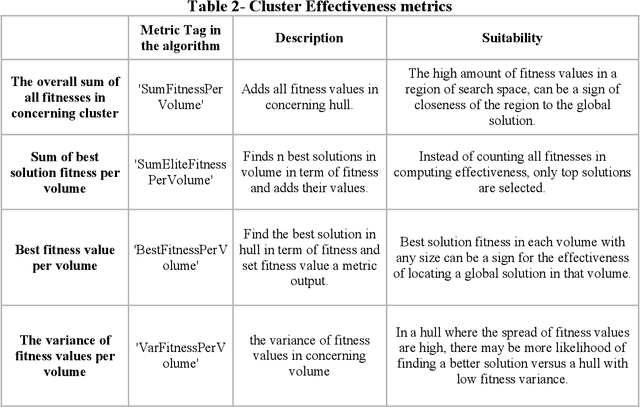
Observer effect in physics (/psychology) regards bias in measurement (/perception) due to the interference of instrument (/knowledge). Based on these concepts, a new meta-heuristic algorithm is proposed for controlling memory usage per localities without pursuing Tabu-like cut-off approaches. In this paper, first, variations of observer effect are explained in different branches of science from physics to psychology. Then, a metaheuristic algorithm is proposed based on observer effect concepts and the used metrics are explained. The derived optimizer performance has been compared between 1st, non-homogeneous-peaks-density functions, and 2nd, homogeneous-peaks-density functions to verify the algorithm outperformance in the 1st scheme. Finally, performance analysis of the novel algorithms is derived using two real-world engineering applications in Electroencephalogram feature learning and Distributed Generator parameter tuning, each of which having nonlinearity and complex multi-modal peaks distributions as its characteristics. Also, the effect of version improvement has been assessed. The performance analysis among other optimizers in the same context suggests that the proposed algorithm is useful both solely and in hybrid Gradient Descent settings where problem's search space is nonhomogeneous in terms of local peaks density.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge