Measuring non-trivial compositionality in emergent communication
Paper and Code
Oct 29, 2020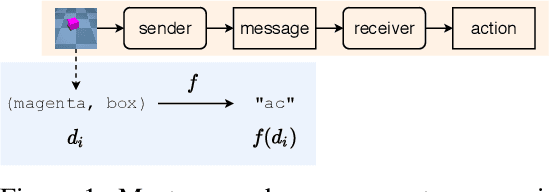
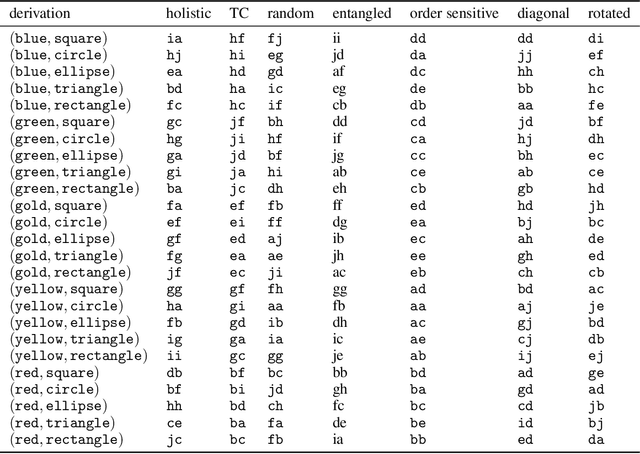
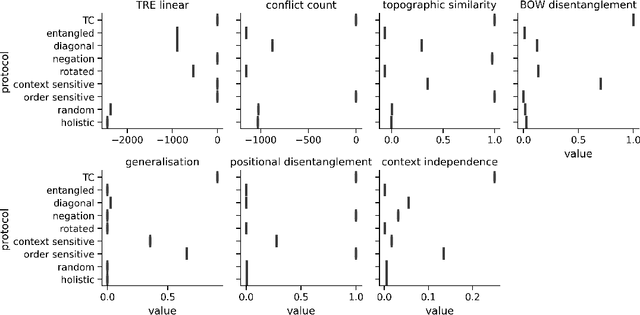
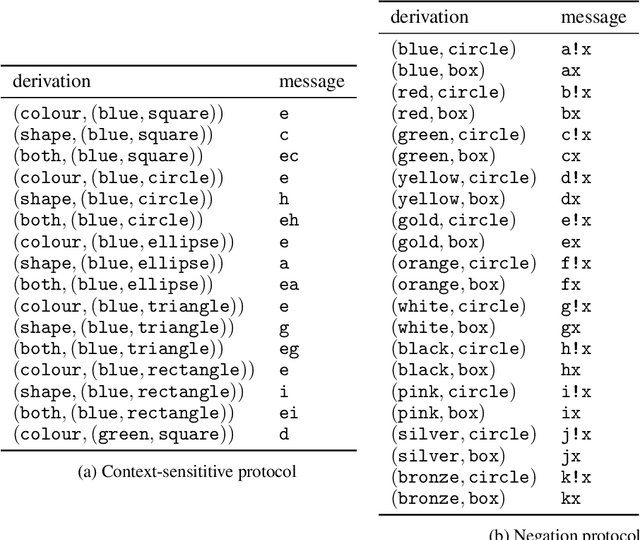
Compositionality is an important explanatory target in emergent communication and language evolution. The vast majority of computational models of communication account for the emergence of only a very basic form of compositionality: trivial compositionality. A compositional protocol is trivially compositional if the meaning of a complex signal (e.g. blue circle) boils down to the intersection of meanings of its constituents (e.g. the intersection of the set of blue objects and the set of circles). A protocol is non-trivially compositional (NTC) if the meaning of a complex signal (e.g. biggest apple) is a more complex function of the meanings of their constituents. In this paper, we review several metrics of compositionality used in emergent communication and experimentally show that most of them fail to detect NTC - i.e. they treat non-trivial compositionality as a failure of compositionality. The one exception is tree reconstruction error, a metric motivated by formal accounts of compositionality. These results emphasise important limitations of emergent communication research that could hamper progress on modelling the emergence of NTC.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge