MaxMI: A Maximal Mutual Information Criterion for Manipulation Concept Discovery
Paper and Code
Jul 21, 2024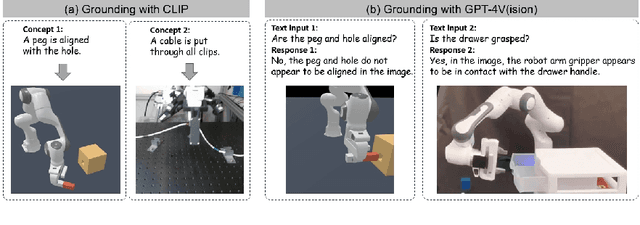
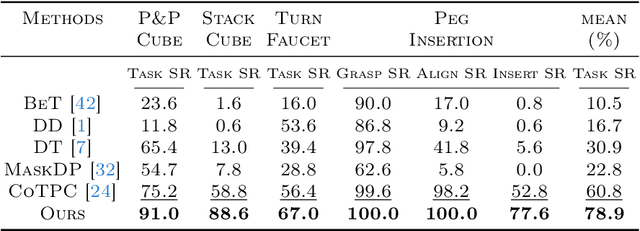
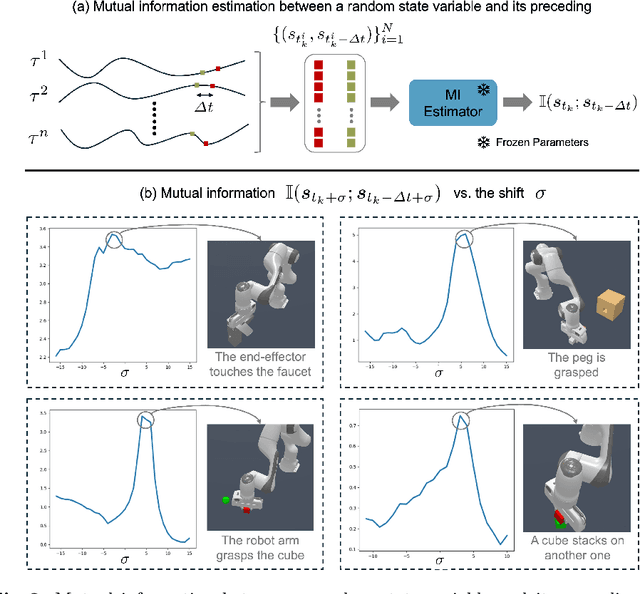
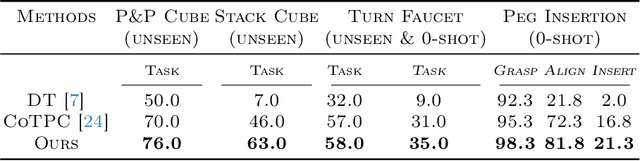
We aim to discover manipulation concepts embedded in the unannotated demonstrations, which are recognized as key physical states. The discovered concepts can facilitate training manipulation policies and promote generalization. Current methods relying on multimodal foundation models for deriving key states usually lack accuracy and semantic consistency due to limited multimodal robot data. In contrast, we introduce an information-theoretic criterion to characterize the regularities that signify a set of physical states. We also develop a framework that trains a concept discovery network using this criterion, thus bypassing the dependence on human semantics and alleviating costly human labeling. The proposed criterion is based on the observation that key states, which deserve to be conceptualized, often admit more physical constraints than non-key states. This phenomenon can be formalized as maximizing the mutual information between the putative key state and its preceding state, i.e., Maximal Mutual Information (MaxMI). By employing MaxMI, the trained key state localization network can accurately identify states of sufficient physical significance, exhibiting reasonable semantic compatibility with human perception. Furthermore, the proposed framework produces key states that lead to concept-guided manipulation policies with higher success rates and better generalization in various robotic tasks compared to the baselines, verifying the effectiveness of the proposed criterion.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge