Matching with Text Data: An Experimental Evaluation of Methods for Matching Documents and of Measuring Match Quality
Paper and Code
Oct 03, 2018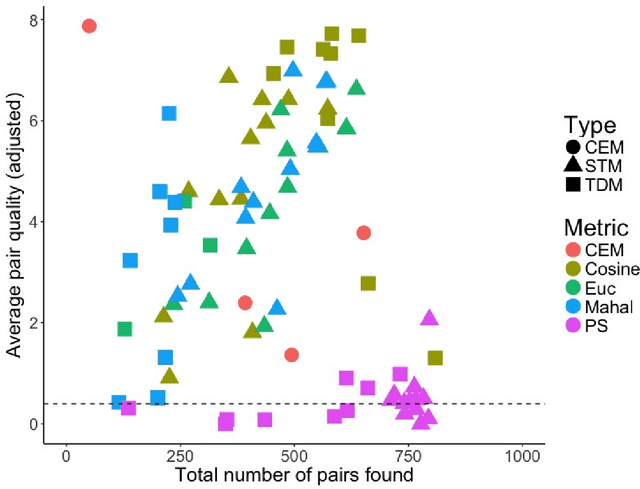
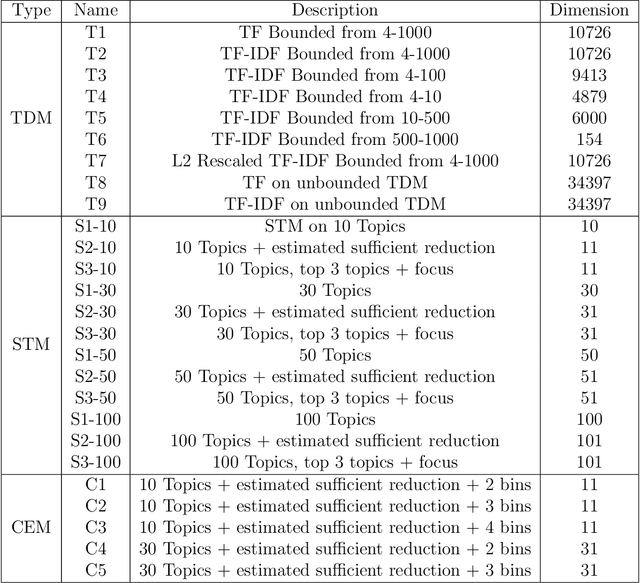
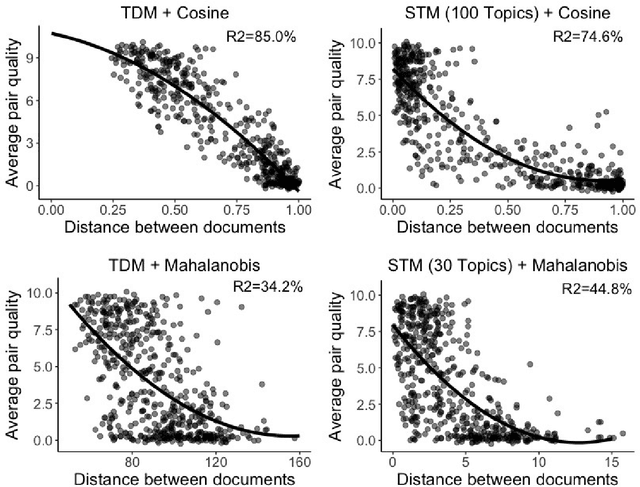
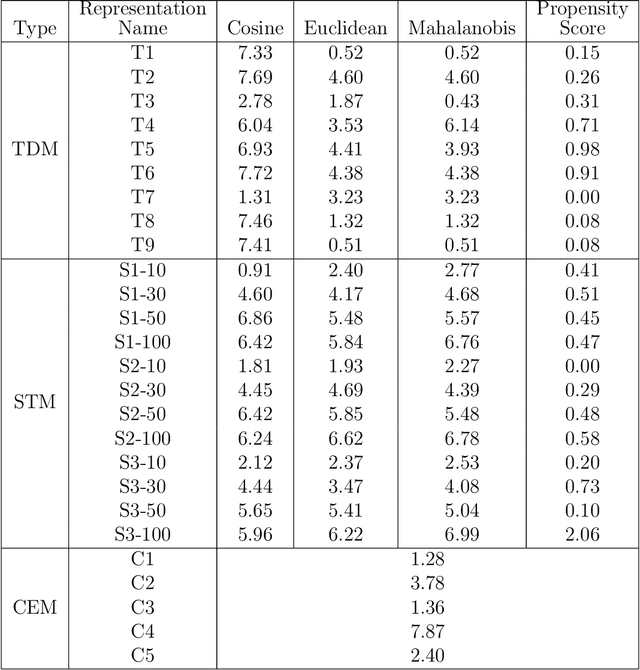
Matching for causal inference is a well-studied problem, but standard methods fail when the units to match are text documents: the high-dimensional and rich nature of the data renders exact matching infeasible, causes propensity scores to produce incomparable matches, and makes assessing match quality difficult. In this paper, we characterize a framework for matching text documents that decomposes existing methods into: (1) the choice of text representation, and (2) the choice of distance metric. We investigate how different choices within this framework affect both the quantity and quality of matches identified through a systematic multifactor evaluation experiment using human subjects. Altogether we evaluate over 100 unique text matching methods along with 5 comparison methods taken from the literature. Our experimental results identify methods that generate matches with higher subjective match quality than current state-of-the-art techniques. We enhance the precision of these results by developing a predictive model to estimate the match quality of pairs of text documents as a function of our various distance scores. This model, which we find successfully mimics human judgment, also allows for approximate and unsupervised evaluation of new procedures. We then employ the identified best method to illustrate the utility of text matching in two applications. First, we engage with a substantive debate in the study of media bias by using text matching to control for topic selection when comparing news articles from thirteen news sources. We then show how conditioning on text data leads to more precise causal inferences in an observational study examining the effects of a medical intervention.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge