Matching via Distance Profiles
Paper and Code
Dec 19, 2023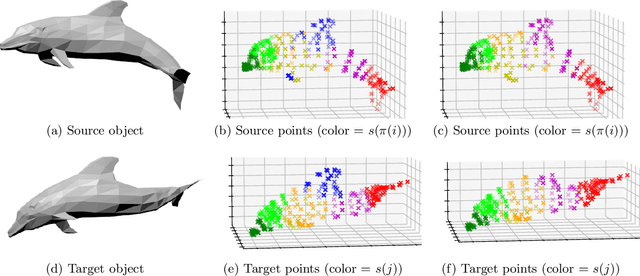
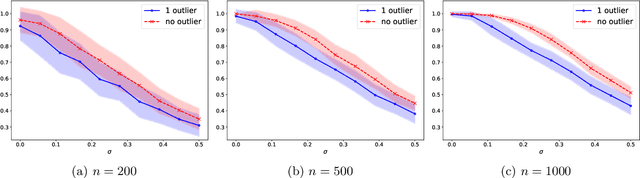

In this paper, we introduce and study matching methods based on distance profiles. For the matching of point clouds, the proposed method is easily implementable by solving a linear program, circumventing the computational obstacles of quadratic matching. Also, we propose and analyze a flexible way to execute location-to-location matching using distance profiles. Moreover, we provide a statistical estimation error analysis in the context of location-to-location matching using empirical process theory. Furthermore, we apply our method to a certain model and show its noise stability by characterizing conditions on the noise level for the matching to be successful. Lastly, we demonstrate the performance of the proposed method and compare it with some existing methods using synthetic and real data.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge