Machine Learning-based Variability Handling in IoT Agents
Paper and Code
Feb 12, 2018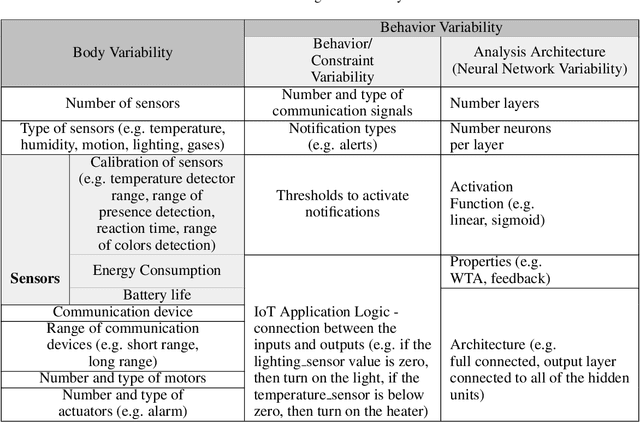
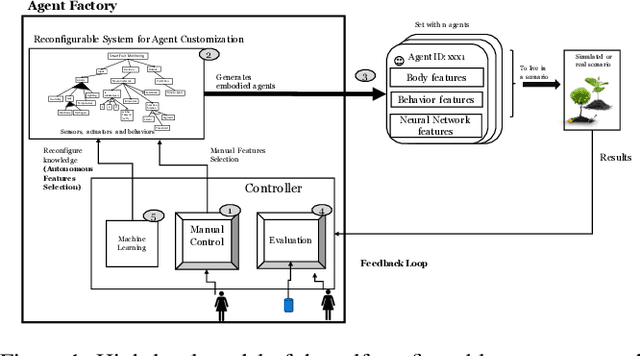
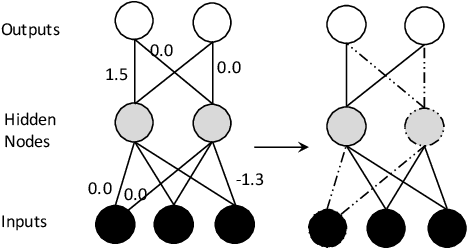
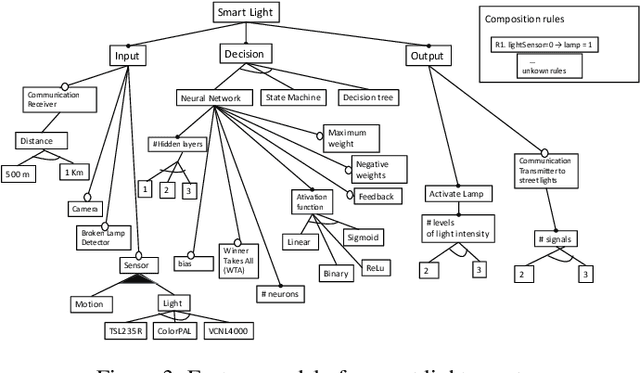
Agent-based IoT applications have recently been proposed in several domains, such as health care, smart cities and agriculture. Deploying these applications in specific settings has been very challenging for many reasons including the complex static and dynamic variability of the physical devices such as sensors and actuators, the software application behavior and the environment in which the application is embedded. In this paper, we propose a self-configurable IoT agent approach based on feedback-evaluative machine-learning. The approach involves: i) a variability model of IoT agents; ii) generation of sets of customized agents; iii) feedback evaluative machine learning; iv) modeling and composition of a group of IoT agents; and v) a feature-selection method based on manual and automatic feedback.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge