LV-UNet: A Lightweight and Vanilla Model for Medical Image Segmentation
Paper and Code
Aug 29, 2024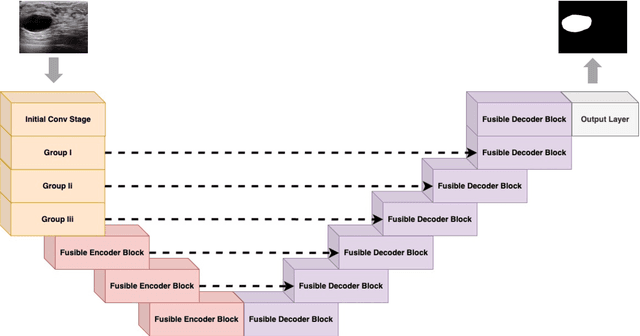
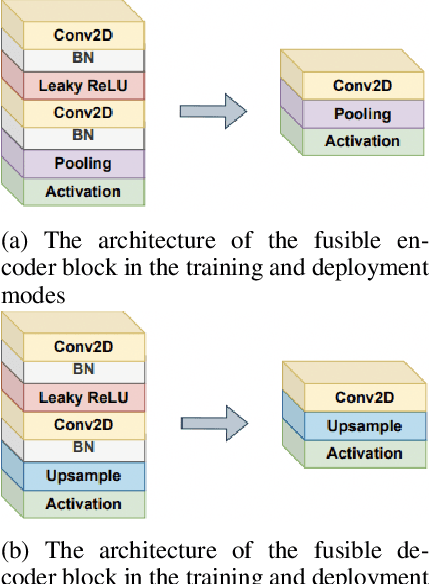
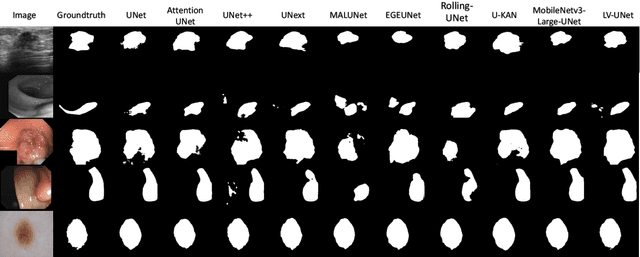
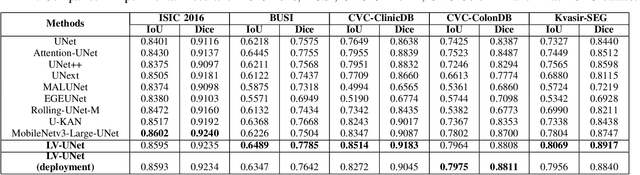
Although the progress made by large models in computer vision, optimization challenges, the complexity of transformer models, computational limitations, and the requirements of practical applications call for simpler designs in model architecture for medical image segmentation, especially in mobile medical devices that require lightweight and deployable models with real-time performance. However, some of the current lightweight models exhibit poor robustness across different datasets, which hinders their broader adoption. This paper proposes a lightweight and vanilla model called LV-UNet, which effectively utilizes pre-trained MobileNetv3-Large models and introduces fusible modules. It can be trained using an improved deep training strategy and switched to deployment mode during inference, reducing both parameter count and computational load. Experiments are conducted on ISIC 2016, BUSI, CVC- ClinicDB, CVC-ColonDB, and Kvair-SEG datasets, achieving better performance compared to the state-of-the-art and classic models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge