Lung Structures Enhancement in Chest Radiographs via CT based FCNN Training
Paper and Code
Oct 14, 2018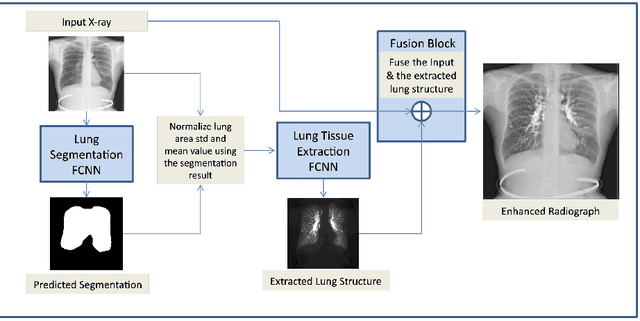
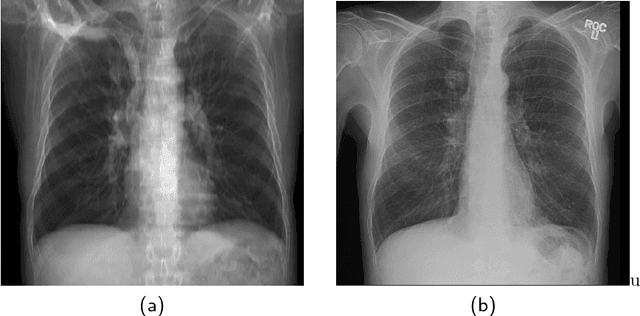
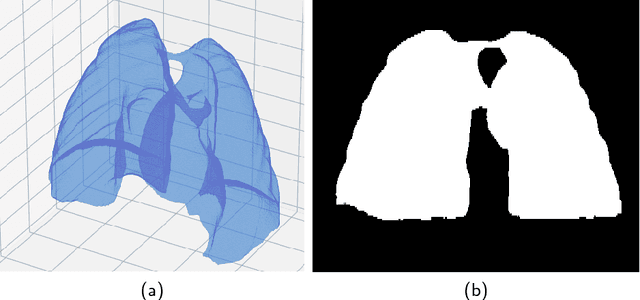
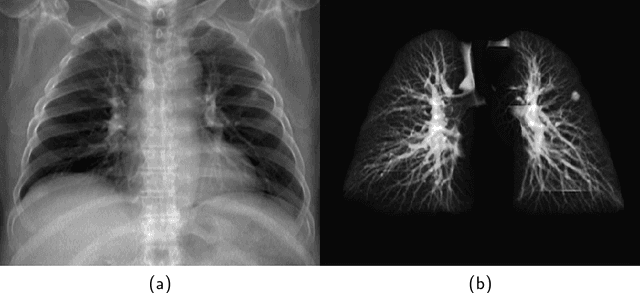
The abundance of overlapping anatomical structures appearing in chest radiographs can reduce the performance of lung pathology detection by automated algorithms (CAD) as well as the human reader. In this paper, we present a deep learning based image processing technique for enhancing the contrast of soft lung structures in chest radiographs using Fully Convolutional Neural Networks (FCNN). Two 2D FCNN architectures were trained to accomplish the task: The first performs 2D lung segmentation which is used for normalization of the lung area. The second FCNN is trained to extract lung structures. To create the training images, we employed Simulated X-Ray or Digitally Reconstructed Radiographs (DRR) derived from 516 scans belonging to the LIDC-IDRI dataset. By first segmenting the lungs in the CT domain, we are able to create a dataset of 2D lung masks to be used for training the segmentation FCNN. For training the extraction FCNN, we create DRR images of only voxels belonging to the 3D lung segmentation which we call "Lung X-ray" and use them as target images. Once the lung structures are extracted, the original image can be enhanced by fusing the original input x-ray and the synthesized "Lung X-ray". We show that our enhancement technique is applicable to real x-ray data, and display our results on the recently released NIH Chest X-Ray-14 dataset. We see promising results when training a DenseNet-121 based architecture to work directly on the lung enhanced X-ray images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge