LSTM Acoustic Models Learn to Align and Pronounce with Graphemes
Paper and Code
Aug 13, 2020

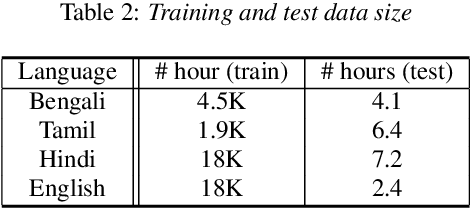
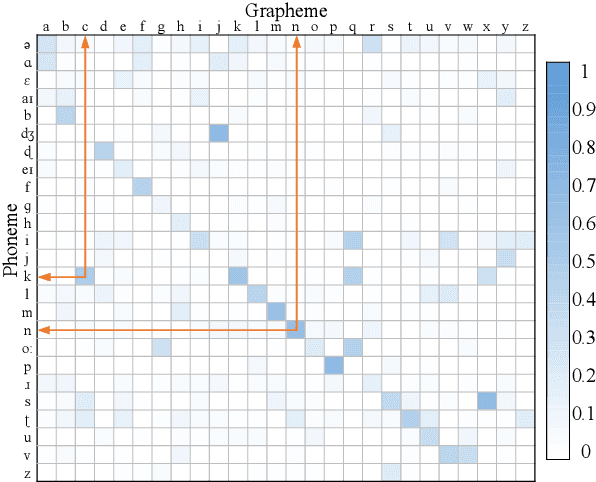
Automated speech recognition coverage of the world's languages continues to expand. However, standard phoneme based systems require handcrafted lexicons that are difficult and expensive to obtain. To address this problem, we propose a training methodology for a grapheme-based speech recognizer that can be trained in a purely data-driven fashion. Built with LSTM networks and trained with the cross-entropy loss, the grapheme-output acoustic models we study are also extremely practical for real-world applications as they can be decoded with conventional ASR stack components such as language models and FST decoders, and produce good quality audio-to-grapheme alignments that are useful in many speech applications. We show that the grapheme models are competitive in WER with their phoneme-output counterparts when trained on large datasets, with the advantage that grapheme models do not require explicit linguistic knowledge as an input. We further compare the alignments generated by the phoneme and grapheme models to demonstrate the quality of the pronunciations learnt by them using four Indian languages that vary linguistically in spoken and written forms.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge