Low-Resource Task-Oriented Semantic Parsing via Intrinsic Modeling
Paper and Code
Apr 15, 2021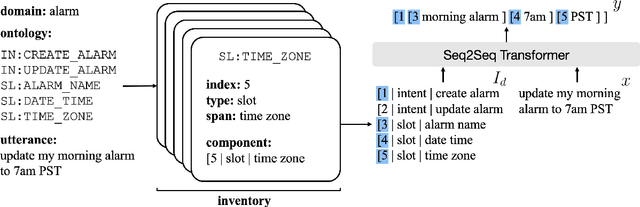
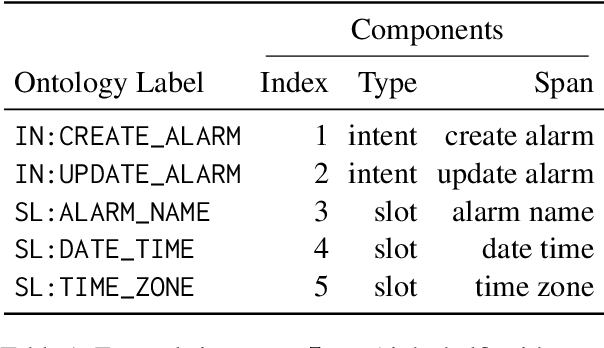
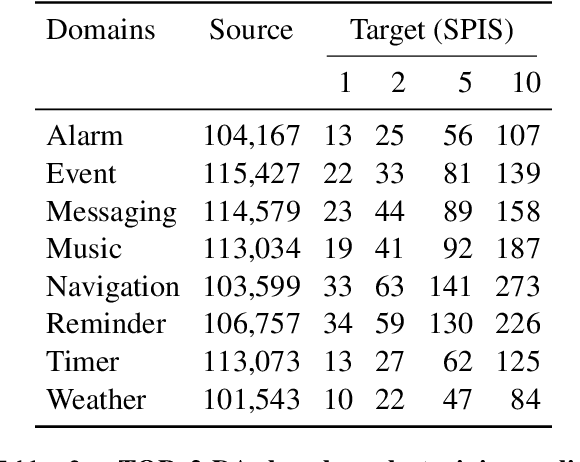
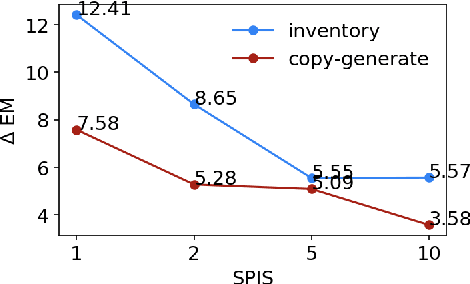
Task-oriented semantic parsing models typically have high resource requirements: to support new ontologies (i.e., intents and slots), practitioners crowdsource thousands of samples for supervised fine-tuning. Partly, this is due to the structure of de facto copy-generate parsers; these models treat ontology labels as discrete entities, relying on parallel data to extrinsically derive their meaning. In our work, we instead exploit what we intrinsically know about ontology labels; for example, the fact that SL:TIME_ZONE has the categorical type "slot" and language-based span "time zone". Using this motivation, we build our approach with offline and online stages. During preprocessing, for each ontology label, we extract its intrinsic properties into a component, and insert each component into an inventory as a cache of sorts. During training, we fine-tune a seq2seq, pre-trained transformer to map utterances and inventories to frames, parse trees comprised of utterance and ontology tokens. Our formulation encourages the model to consider ontology labels as a union of its intrinsic properties, therefore substantially bootstrapping learning in low-resource settings. Experiments show our model is highly sample efficient: using a low-resource benchmark derived from TOPv2, our inventory parser outperforms a copy-generate parser by +15 EM absolute (44% relative) when fine-tuning on 10 samples from an unseen domain.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge