Long-tailed Extreme Multi-label Text Classification with Generated Pseudo Label Descriptions
Paper and Code
Apr 02, 2022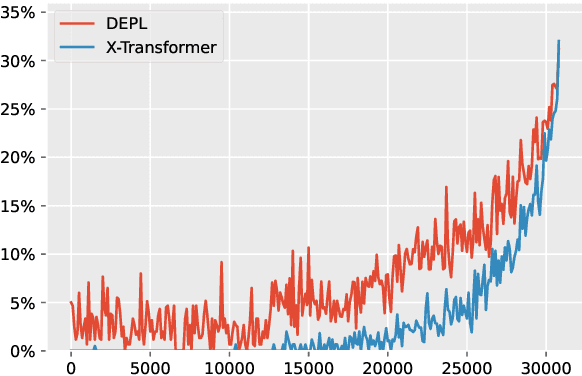
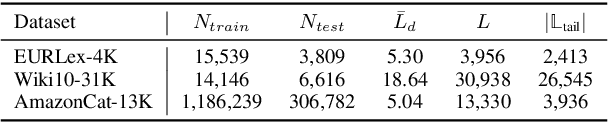
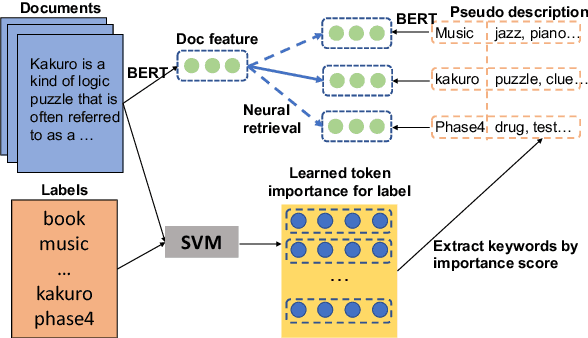
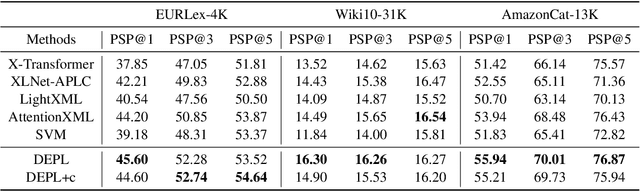
Extreme Multi-label Text Classification (XMTC) has been a tough challenge in machine learning research and applications due to the sheer sizes of the label spaces and the severe data scarce problem associated with the long tail of rare labels in highly skewed distributions. This paper addresses the challenge of tail label prediction by proposing a novel approach, which combines the effectiveness of a trained bag-of-words (BoW) classifier in generating informative label descriptions under severe data scarce conditions, and the power of neural embedding based retrieval models in mapping input documents (as queries) to relevant label descriptions. The proposed approach achieves state-of-the-art performance on XMTC benchmark datasets and significantly outperforms the best methods so far in the tail label prediction. We also provide a theoretical analysis for relating the BoW and neural models w.r.t. performance lower bound.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge