Logical Negation Augmenting and Debiasing for Prompt-based Methods
Paper and Code
May 08, 2024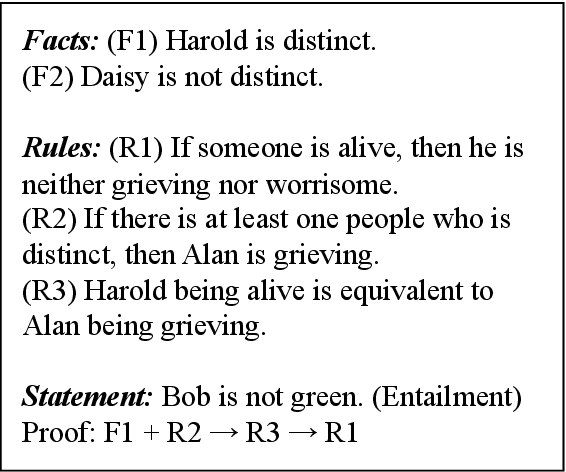
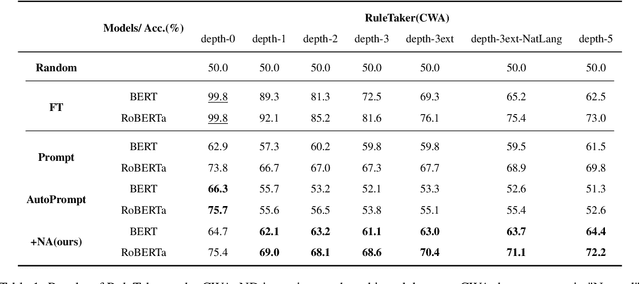
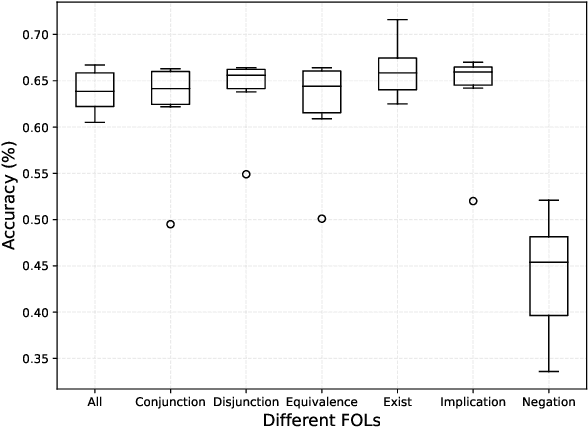
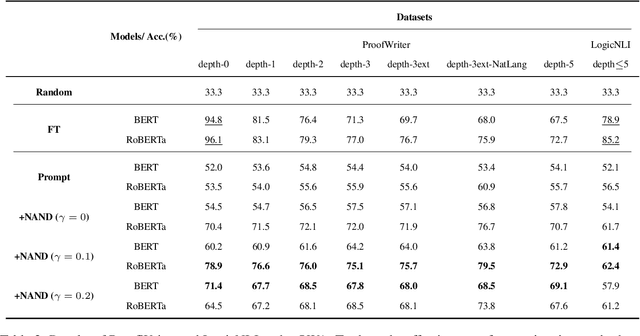
Prompt-based methods have gained increasing attention on NLP and shown validity on many downstream tasks. Many works have focused on mining these methods' potential for knowledge extraction, but few explore their ability to make logical reasoning. In this work, we focus on the effectiveness of the prompt-based methods on first-order logical reasoning and find that the bottleneck lies in logical negation. Based on our analysis, logical negation tends to result in spurious correlations to negative answers, while propositions without logical negation correlate to positive answers. To solve the problem, we propose a simple but effective method, Negation Augmenting and Negation Debiasing (NAND), which introduces negative propositions to prompt-based methods without updating parameters. Specifically, these negative propositions can counteract spurious correlations by providing "not" for all instances so that models cannot make decisions only by whether expressions contain a logical negation. Experiments on three datasets show that NAND not only solves the problem of calibrating logical negation but also significantly enhances prompt-based methods of logical reasoning without model retraining.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge