Localized Dictionary design for Geometrically Robust Sonar ATR
Paper and Code
Jan 13, 2016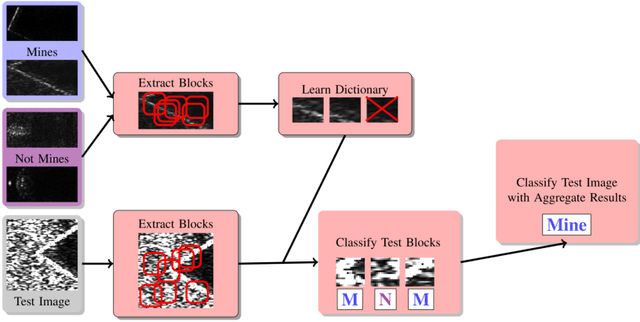
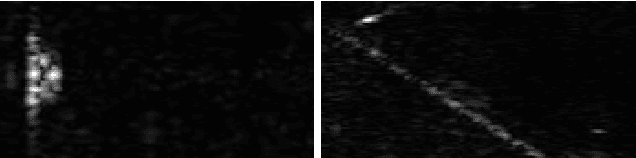
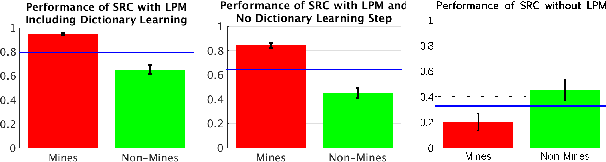
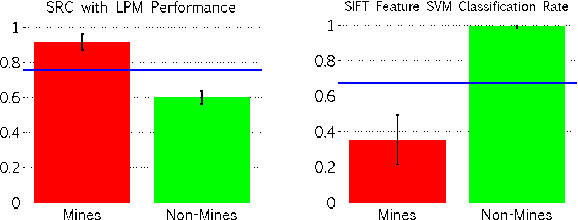
Advancements in Sonar image capture have opened the door to powerful classification schemes for automatic target recognition (ATR. Recent work has particularly seen the application of sparse reconstruction-based classification (SRC) to sonar ATR, which provides compelling accuracy rates even in the presence of noise and blur. Existing sparsity based sonar ATR techniques however assume that the test images exhibit geometric pose that is consistent with respect to the training set. This work addresses the outstanding open challenge of handling inconsistently posed test sonar images relative to training. We develop a new localized block-based dictionary design that can enable geometric, i.e. pose robustness. Further, a dictionary learning method is incorporated to increase performance and efficiency. The proposed SRC with Localized Pose Management (LPM), is shown to outperform the state of the art SIFT feature and SVM approach, due to its power to discern background clutter in Sonar images.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge