Localization of Autonomous Vehicles: Proof of Concept for A Computer Vision Approach
Paper and Code
Apr 06, 2021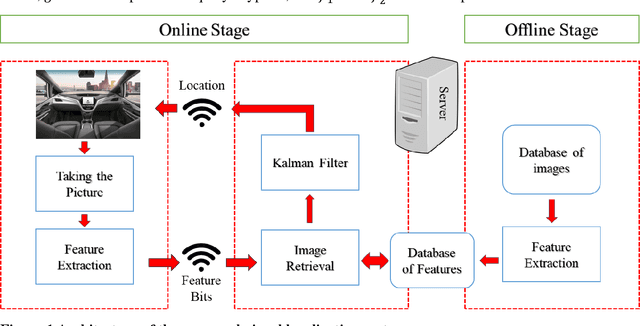


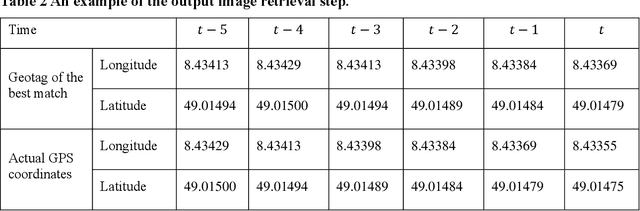
This paper introduces a visual-based localization method for autonomous vehicles (AVs) that operate in the absence of any complicated hardware system but a single camera. Visual localization refers to techniques that aim to find the location of an object based on visual information of its surrounding area. The problem of localization has been of interest for many years. However, visual localization is a relatively new subject in the literature of transportation. Moreover, the inevitable application of this type of localization in the context of autonomous vehicles demands special attention from the transportation community to this problem. This study proposes a two-step localization method that requires a database of geotagged images and a camera mounted on a vehicle that can take pictures while the car is moving. The first step which is image retrieval uses SIFT local feature descriptor to find an initial location for the vehicle using image matching. The next step is to utilize the Kalman filter to estimate a more accurate location for the vehicle as it is moving. All stages of the introduced method are implemented as a complete system using different Python libraries. The proposed system is tested on the KITTI dataset and has shown an average accuracy of 2 meters in finding the final location of the vehicle.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge