Locality and low-dimensions in the prediction of natural experience from fMRI
Paper and Code
Jan 12, 2008
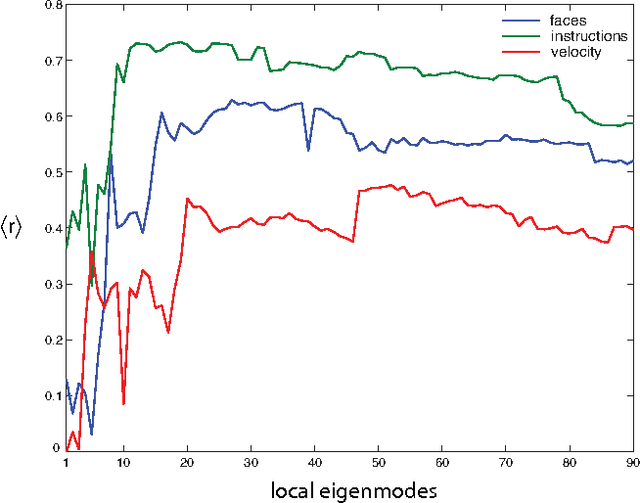
Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging (fMRI) provides dynamical access into the complex functioning of the human brain, detailing the hemodynamic activity of thousands of voxels during hundreds of sequential time points. One approach towards illuminating the connection between fMRI and cognitive function is through decoding; how do the time series of voxel activities combine to provide information about internal and external experience? Here we seek models of fMRI decoding which are balanced between the simplicity of their interpretation and the effectiveness of their prediction. We use signals from a subject immersed in virtual reality to compare global and local methods of prediction applying both linear and nonlinear techniques of dimensionality reduction. We find that the prediction of complex stimuli is remarkably low-dimensional, saturating with less than 100 features. In particular, we build effective models based on the decorrelated components of cognitive activity in the classically-defined Brodmann areas. For some of the stimuli, the top predictive areas were surprisingly transparent, including Wernicke's area for verbal instructions, visual cortex for facial and body features, and visual-temporal regions for velocity. Direct sensory experience resulted in the most robust predictions, with the highest correlation ($c \sim 0.8$) between the predicted and experienced time series of verbal instructions. Techniques based on non-linear dimensionality reduction (Laplacian eigenmaps) performed similarly. The interpretability and relative simplicity of our approach provides a conceptual basis upon which to build more sophisticated techniques for fMRI decoding and offers a window into cognitive function during dynamic, natural experience.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge