Local-Global Associative Frame Assemble in Video Re-ID
Paper and Code
Oct 22, 2021
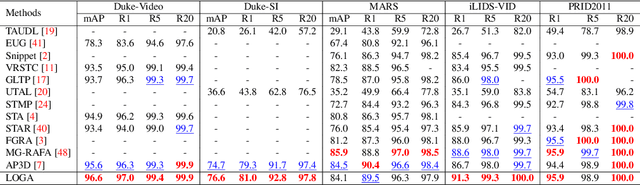
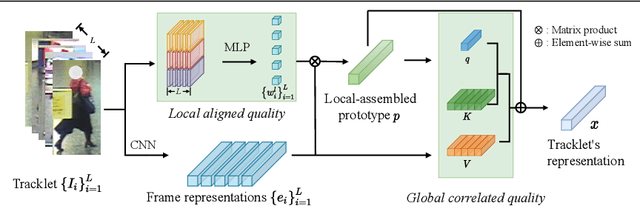

Noisy and unrepresentative frames in automatically generated object bounding boxes from video sequences cause significant challenges in learning discriminative representations in video re-identification (Re-ID). Most existing methods tackle this problem by assessing the importance of video frames according to either their local part alignments or global appearance correlations separately. However, given the diverse and unknown sources of noise which usually co-exist in captured video data, existing methods have not been effective satisfactorily. In this work, we explore jointly both local alignments and global correlations with further consideration of their mutual promotion/reinforcement so to better assemble complementary discriminative Re-ID information within all the relevant frames in video tracklets. Specifically, we concurrently optimise a local aligned quality (LAQ) module that distinguishes the quality of each frame based on local alignments, and a global correlated quality (GCQ) module that estimates global appearance correlations. With the help of a local-assembled global appearance prototype, we associate LAQ and GCQ to exploit their mutual complement. Extensive experiments demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model against state-of-the-art methods on five Re-ID benchmarks, including MARS, Duke-Video, Duke-SI, iLIDS-VID, and PRID2011.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge