Local Collaborative Autoencoders
Paper and Code
Mar 30, 2021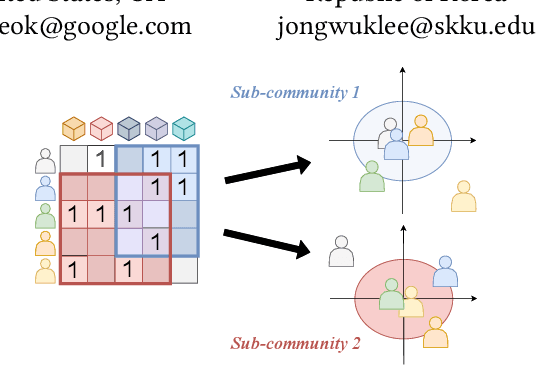
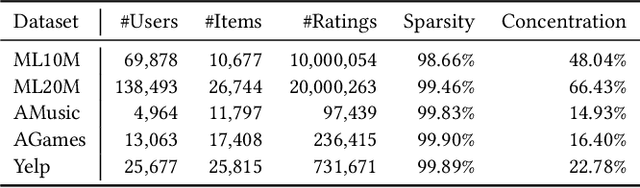
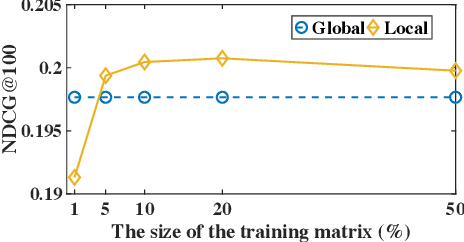
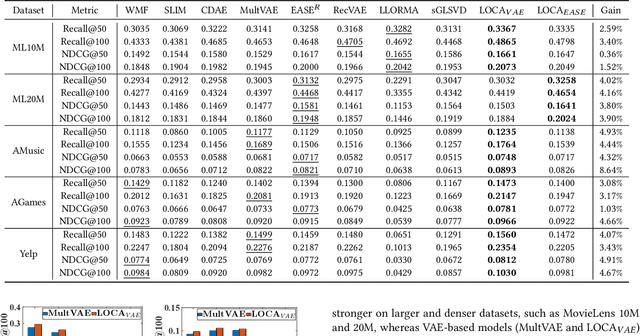
Top-N recommendation is a challenging problem because complex and sparse user-item interactions should be adequately addressed to achieve high-quality recommendation results. The local latent factor approach has been successfully used with multiple local models to capture diverse user preferences with different sub-communities. However, previous studies have not fully explored the potential of local models, and failed to identify many small and coherent sub-communities. In this paper, we present Local Collaborative Autoencoders (LOCA), a generalized local latent factor framework. Specifically, LOCA adopts different neighborhood ranges at the training and inference stages. Besides, LOCA uses a novel sub-community discovery method, maximizing the coverage of a union of local models and employing a large number of diverse local models. By adopting autoencoders as the base model, LOCA captures latent non-linear patterns representing meaningful user-item interactions within sub-communities. Our experimental results demonstrate that LOCA is scalable and outperforms state-of-the-art models on several public benchmarks, by 2.99~4.70% in Recall and 1.02~7.95% in NDCG, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge