Load Embeddings for Scalable AC-OPF Learning
Paper and Code
Jan 11, 2021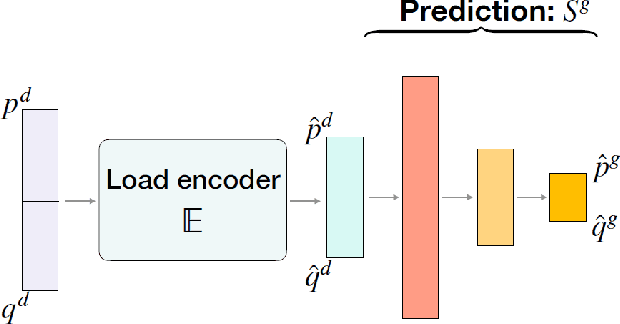

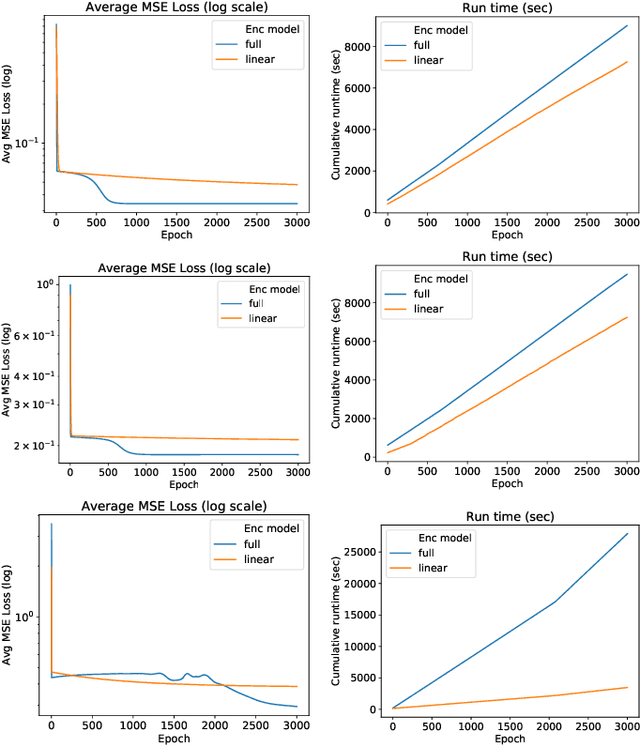
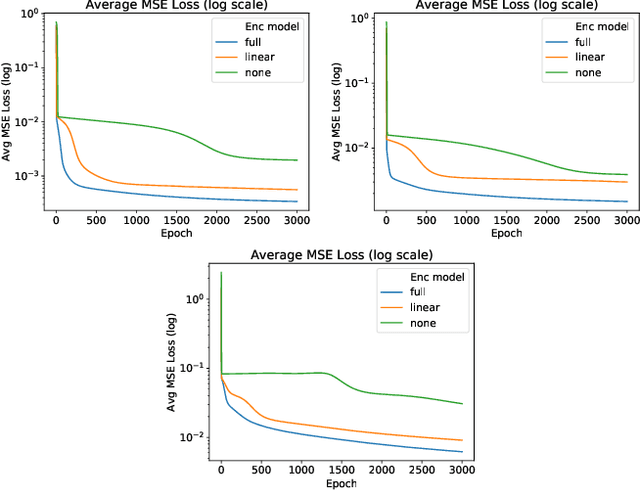
AC Optimal Power Flow (AC-OPF) is a fundamental building block in power system optimization. It is often solved repeatedly, especially in regions with large penetration of renewable generation, to avoid violating operational limits. Recent work has shown that deep learning can be effective in providing highly accurate approximations of AC-OPF. However, deep learning approaches may suffer from scalability issues, especially when applied to large realistic grids. This paper addresses these scalability limitations and proposes a load embedding scheme using a 3-step approach. The first step formulates the load embedding problem as a bilevel optimization model that can be solved using a penalty method. The second step learns the encoding optimization to quickly produce load embeddings for new OPF instances. The third step is a deep learning model that uses load embeddings to produce accurate AC-OPF approximations. The approach is evaluated experimentally on large-scale test cases from the NESTA library. The results demonstrate that the proposed approach produces an order of magnitude improvements in training convergence and prediction accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge