Lifelong Learning Using a Dynamically Growing Tree of Sub-networks for Domain Generalization in Video Object Segmentation
Paper and Code
May 29, 2024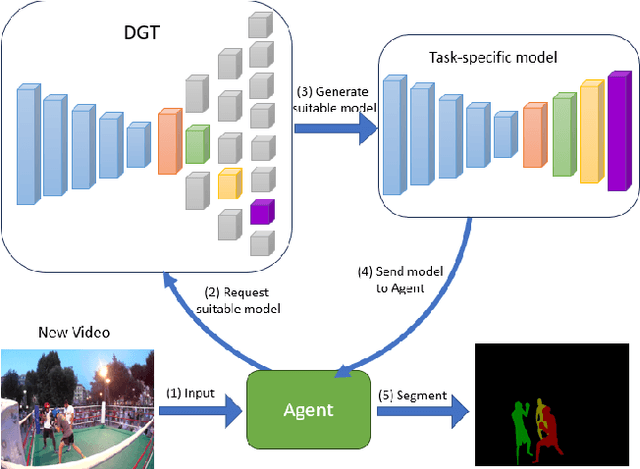
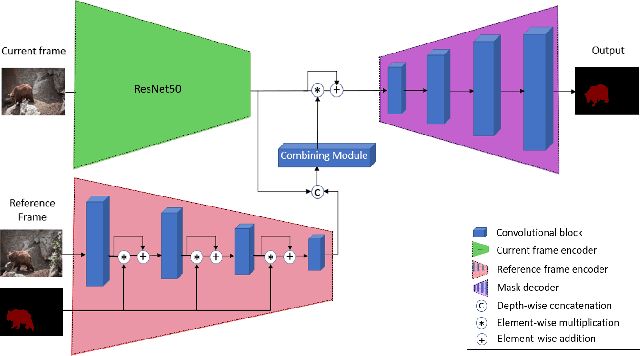
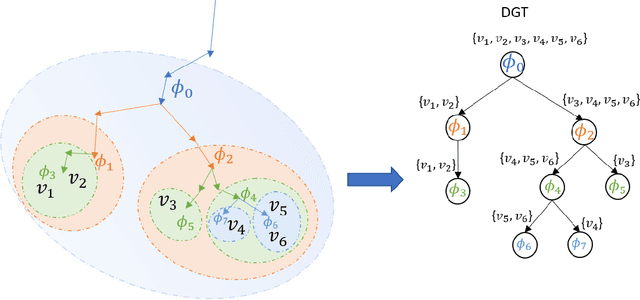
Current state-of-the-art video object segmentation models have achieved great success using supervised learning with massive labeled training datasets. However, these models are trained using a single source domain and evaluated using videos sampled from the same source domain. When these models are evaluated using videos sampled from a different target domain, their performance degrades significantly due to poor domain generalization, i.e., their inability to learn from multi-domain sources simultaneously using traditional supervised learning. In this paper, We propose a dynamically growing tree of sub-networks (DGT) to learn effectively from multi-domain sources. DGT uses a novel lifelong learning technique that allows the model to continuously and effectively learn from new domains without forgetting the previously learned domains. Hence, the model can generalize to out-of-domain videos. The proposed work is evaluated using single-source in-domain (traditional video object segmentation), multi-source in-domain, and multi-source out-of-domain video object segmentation. The results of DGT show a single source in-domain performance gain of 0.2% and 3.5% on the DAVIS16 and DAVIS17 datasets, respectively. However, when DGT is evaluated using in-domain multi-sources, the results show superior performance compared to state-of-the-art video object segmentation and other lifelong learning techniques with an average performance increase in the F-score of 6.9% with minimal catastrophic forgetting. Finally, in the out-of-domain experiment, the performance of DGT is 2.7% and 4% better than state-of-the-art in 1 and 5-shots, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge