Leveraging Time-Series Foundation Models in Smart Agriculture for Soil Moisture Forecasting
Paper and Code
May 29, 2024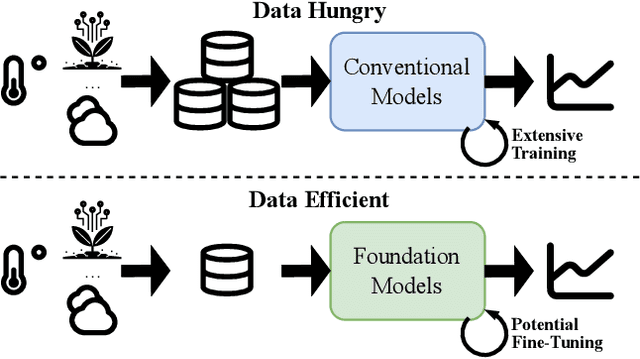
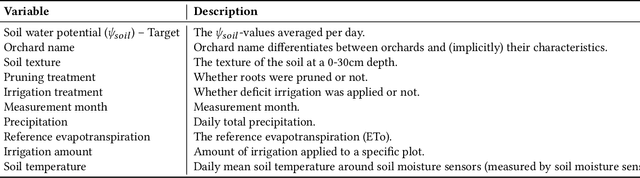

The recent surge in foundation models for natural language processing and computer vision has fueled innovation across various domains. Inspired by this progress, we explore the potential of foundation models for time-series forecasting in smart agriculture, a field often plagued by limited data availability. Specifically, this work presents a novel application of $\texttt{TimeGPT}$, a state-of-the-art (SOTA) time-series foundation model, to predict soil water potential ($\psi_\mathrm{soil}$), a key indicator of field water status that is typically used for irrigation advice. Traditionally, this task relies on a wide array of input variables. We explore $\psi_\mathrm{soil}$'s ability to forecast $\psi_\mathrm{soil}$ in: ($i$) a zero-shot setting, ($ii$) a fine-tuned setting relying solely on historic $\psi_\mathrm{soil}$ measurements, and ($iii$) a fine-tuned setting where we also add exogenous variables to the model. We compare $\texttt{TimeGPT}$'s performance to established SOTA baseline models for forecasting $\psi_\mathrm{soil}$. Our results demonstrate that $\texttt{TimeGPT}$ achieves competitive forecasting accuracy using only historical $\psi_\mathrm{soil}$ data, highlighting its remarkable potential for agricultural applications. This research paves the way for foundation time-series models for sustainable development in agriculture by enabling forecasting tasks that were traditionally reliant on extensive data collection and domain expertise.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge