Leveraging the Doppler Effect for Channel Charting
Paper and Code
Apr 15, 2024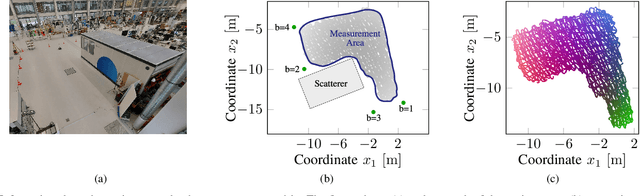
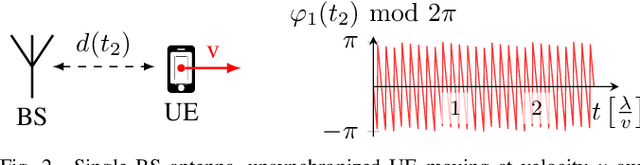
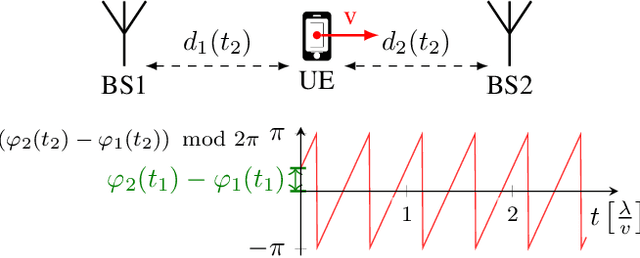
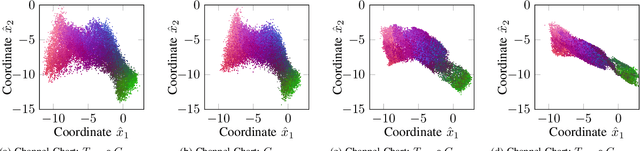
Channel Charting is a dimensionality reduction technique that reconstructs a map of the radio environment from similarity relationships found in channel state information. Distances in the channel chart are often computed based on some dissimilarity metric, which can be derived from angular-domain information, channel impulse responses, measured phase differences or simply timestamps. Using such information implicitly makes strong assumptions about the level of phase and time synchronization between base station antennas or assumes approximately constant transmitter velocity. Many practical systems, however, may not provide phase and time synchronization and single-antenna base stations may not even have angular-domain information. We propose a Doppler effect-based loss function for Channel Charting that only requires frequency synchronization between spatially distributed base station antennas, which is a much weaker assumption. We use a dataset measured in an indoor environment to demonstrate that the proposed method is practically feasible with just four base station antennas, that it produces a channel chart that is suitable for localization in the global coordinate frame and that it outperforms other state-of-the-art methods under the given limitations.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge