Leveraging Privacy Profiles to Empower Users in the Digital Society
Paper and Code
Apr 01, 2022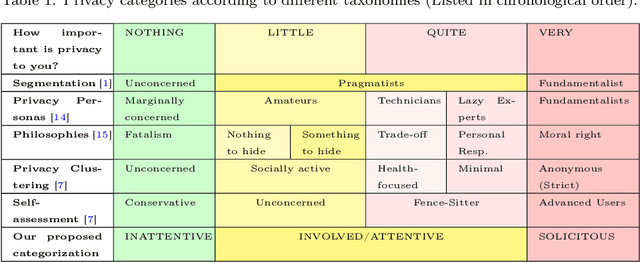
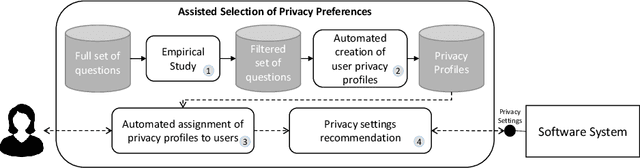
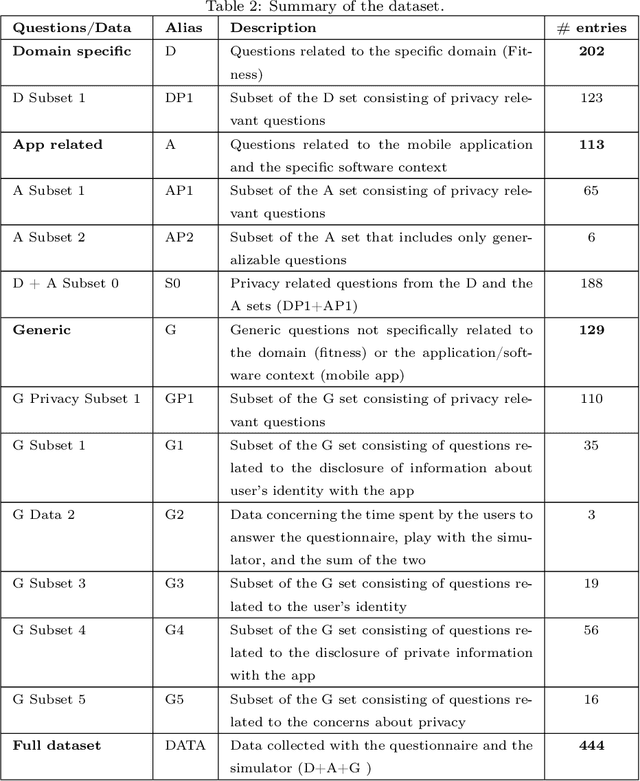
Privacy and ethics of citizens are at the core of the concerns raised by our increasingly digital society. Profiling users is standard practice for software applications triggering the need for users, also enforced by laws, to properly manage privacy settings. Users need to manage software privacy settings properly to protect personally identifiable information and express personal ethical preferences. AI technologies that empower users to interact with the digital world by reflecting their personal ethical preferences can be key enablers of a trustworthy digital society. We focus on the privacy dimension and contribute a step in the above direction through an empirical study on an existing dataset collected from the fitness domain. We find out which set of questions is appropriate to differentiate users according to their preferences. The results reveal that a compact set of semantic-driven questions (about domain-independent privacy preferences) helps distinguish users better than a complex domain-dependent one. This confirms the study's hypothesis that moral attitudes are the relevant piece of information to collect. Based on the outcome, we implement a recommender system to provide users with suitable recommendations related to privacy choices. We then show that the proposed recommender system provides relevant settings to users, obtaining high accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge