Leveraging high-resolution spatial features in mid-infrared spectroscopic imaging to classify tissue subtypes in ovarian cancer
Paper and Code
May 19, 2022

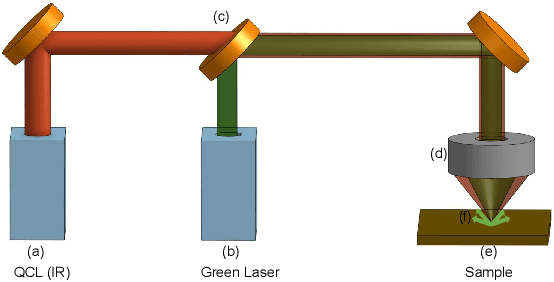

Mid-infrared spectroscopic imaging (MIRSI) is an emerging class of label-free techniques being leveraged for digital histopathology. Optical photothermal infrared (O-PTIR) is based on vibrational absorbance imaging using a pump-probe architecture capable of a 10x enhancement in spatial resolution relative to FTIR imaging. This allows truly sub-cellular spectroscopic investigation of tissue at biochemically important fingerprint wavelengths. Modern histopathologic identification of ovarian cancer involves tissue staining followed by morphological pattern recognition. This process is time-consuming, subjective, and requires extensive expertise. In this paper, we present the first label-free automated histological classification of ovarian tissue sub-types using MIRSI. We demonstrate that enhanced resolution of sub-cellular features, combined with spectroscopic information, enables reliable classification (0.98 AUC) of ovarian cell sub-types. Moreover, we present statistically robust validation from 74 patient samples with over 60 million data points. This demonstrates that sub-cellular resolution from five wavenumbers is sufficient to outperform state-of-the-art diffraction-limited techniques from up to 374 different wavenumbers. O-PTIR also performs measurements in back-reflection geometry, opening the door to future in vivo studies on glass slides.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge