Leveraging A Variety of Anchors in Cellular Network for Ubiquitous Sensing
Paper and Code
Mar 26, 2024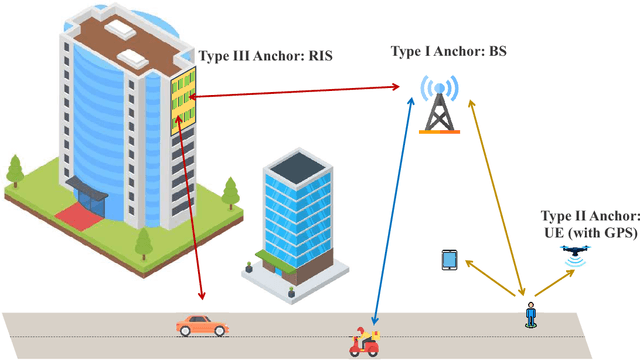
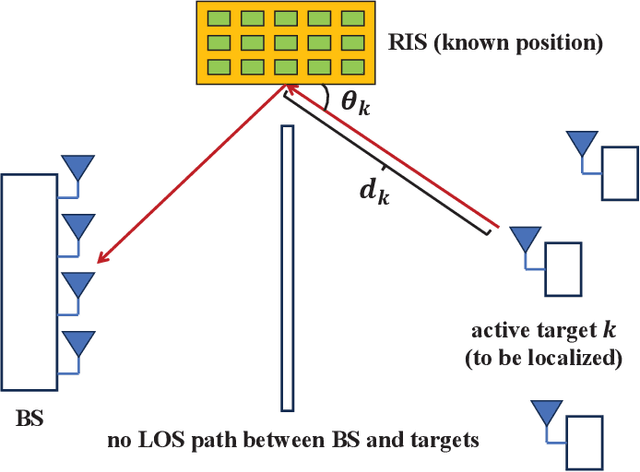
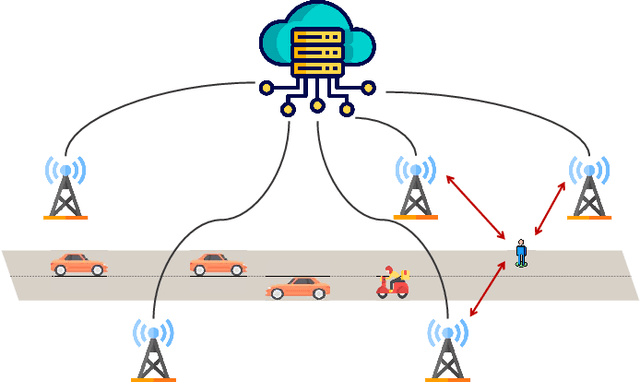
Integrated sensing and communication (ISAC) has recently attracted tremendous attention from both academia and industry, being envisioned as a key part of the standards for the sixth-generation (6G) cellular network. A key challenge of 6G-oriented ISAC lies in how to perform ubiquitous sensing based on the communication signals and devices. Previous works have made great progresses on studying the signal waveform design that leads to optimal communication-sensing performance tradeoff. In this article, we aim to focus on issues arising from the exploitation of the communication devices for sensing in 6G network. Particularly, we will discuss about how to leverage various nodes available in the cellular network as anchors to perform ubiquitous sensing. On one hand, the base stations (BSs) will be the most important anchors in the future 6G ISAC network, since they can generate/process radio signals with high range/angle resolutions, and their positions are precisely known. Correspondingly, we will first study the BS-based sensing technique. On the other hand, the BSs alone may not enable ubiquitous sensing, since they cannot cover all the places with strong line-of-sight (LOS) links. This motivates us to investigate the possibility of using other nodes that are with higher density in the network to act as the anchors. Along this line, we are interested in two types of new anchors - user equipments (UEs) and reconfigurable intelligent surfaces (RISs). This paper will shed light on the opportunities and challenges brought by UE-assisted sensing and RIS-assisted sensing. Our goal is to devise a novel 6G-oriented sensing architecture where BSs, UEs, and RISs can work together to provide ubiquitous sensing services.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge