Let's Push Things Forward: A Survey on Robot Pushing
Paper and Code
May 13, 2019


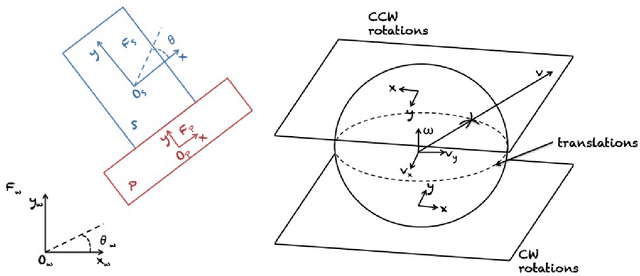
As robot make their way out of factories into human environments, outer space, and beyond, they require the skill to manipulate their environment in multifarious, unforeseeable circumstances. With this regard, pushing is an essential motion primitive that dramatically extends a robot's manipulation repertoire. In this work, we review the robotic pushing literature. While focusing on work concerned with predicting the motion of pushed objects, we also cover relevant applications of pushing for planning and control. Beginning with analytical approaches, under which we also subsume physics engines, we then proceed to discuss work on learning models from data. In doing so, we dedicate a separate section to deep learning approaches which have seen a recent upsurge in the literature. Concluding remarks and further research perspectives are given at the end of the paper.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge