Learning to Communicate with Strangers via Channel Randomisation Methods
Paper and Code
Apr 19, 2021
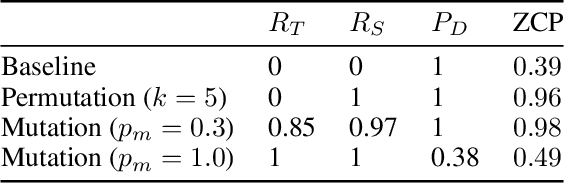


We introduce two methods for improving the performance of agents meeting for the first time to accomplish a communicative task. The methods are: (1) `message mutation' during the generation of the communication protocol; and (2) random permutations of the communication channel. These proposals are tested using a simple two-player game involving a `teacher' who generates a communication protocol and sends a message, and a `student' who interprets the message. After training multiple agents via self-play we analyse the performance of these agents when they are matched with a stranger, i.e. their zero-shot communication performance. We find that both message mutation and channel permutation positively influence performance, and we discuss their effects.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge