Learning the Ordering of Coordinate Compounds and Elaborate Expressions in Hmong, Lahu, and Chinese
Paper and Code
Apr 08, 2022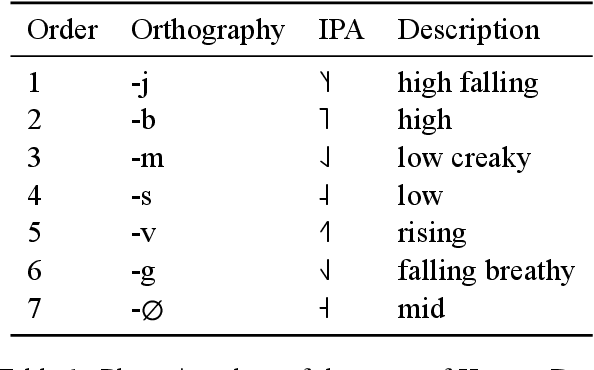
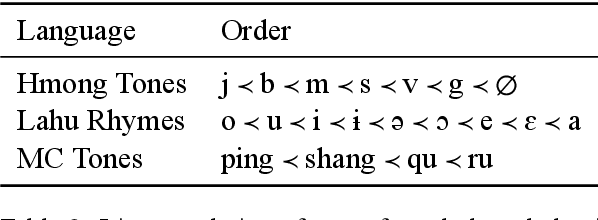
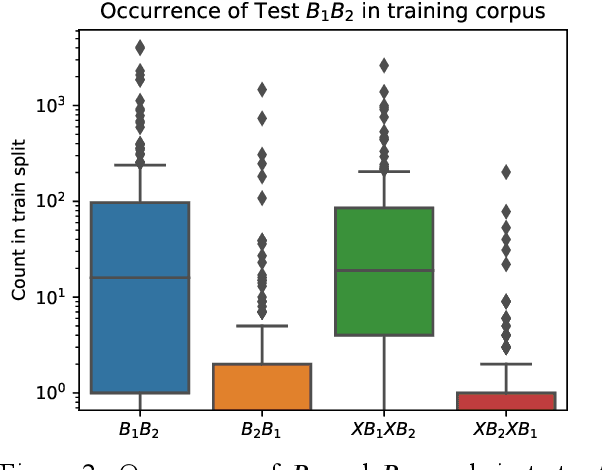
Coordinate compounds (CCs) and elaborate expressions (EEs) are coordinate constructions common in languages of East and Southeast Asia. Mortensen (2006) claims that (1) the linear ordering of EEs and CCs in Hmong, Lahu, and Chinese can be predicted via phonological hierarchies and (2) these phonological hierarchies lack a clear phonetic rationale. These claims are significant because morphosyntax has often been seen as in a feed-forward relationship with phonology, and phonological generalizations have often been assumed to be phonetically "natural". We investigate whether the ordering of CCs and EEs can be learned empirically and whether computational models (classifiers and sequence labeling models) learn unnatural hierarchies similar to those posited by Mortensen (2006). We find that decision trees and SVMs learn to predict the order of CCs/EEs on the basis of phonology, with DTs learning hierarchies strikingly similar to those proposed by Mortensen. However, we also find that a neural sequence labeling model is able to learn the ordering of elaborate expressions in Hmong very effectively without using any phonological information. We argue that EE ordering can be learned through two independent routes: phonology and lexical distribution, presenting a more nuanced picture than previous work. [ISO 639-3:hmn, lhu, cmn]
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge