Learning Invariances for Interpretability using Supervised VAE
Paper and Code
Jul 15, 2020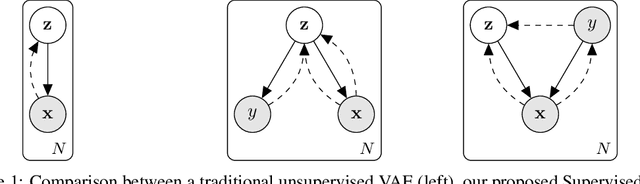

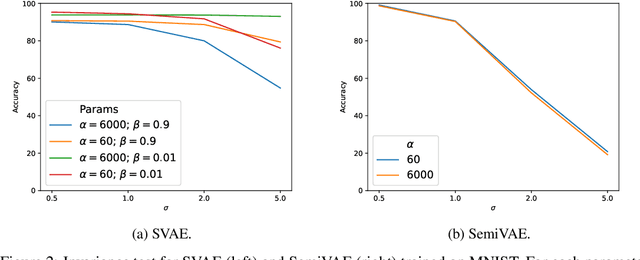

We propose to learn model invariances as a means of interpreting a model. This is motivated by a reverse engineering principle. If we understand a problem, we may introduce inductive biases in our model in the form of invariances. Conversely, when interpreting a complex supervised model, we can study its invariances to understand how that model solves a problem. To this end we propose a supervised form of variational auto-encoders (VAEs). Crucially, only a subset of the dimensions in the latent space contributes to the supervised task, allowing the remaining dimensions to act as nuisance parameters. By sampling solely the nuisance dimensions, we are able to generate samples that have undergone transformations that leave the classification unchanged, revealing the invariances of the model. Our experimental results show the capability of our proposed model both in terms of classification, and generation of invariantly transformed samples. Finally we show how combining our model with feature attribution methods it is possible to reach a more fine-grained understanding about the decision process of the model.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge