Language vs Speaker Change: A Comparative Study
Paper and Code
Mar 05, 2022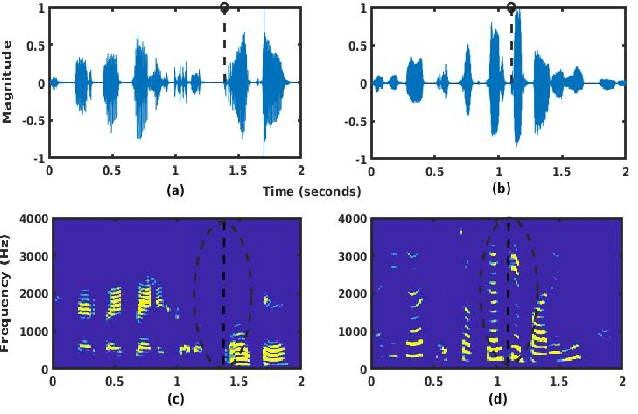
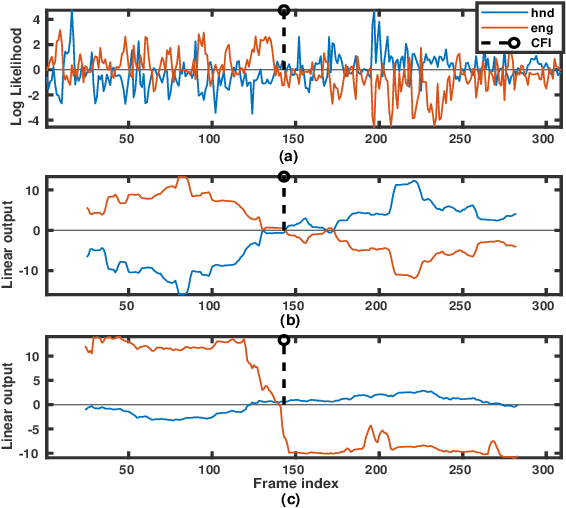
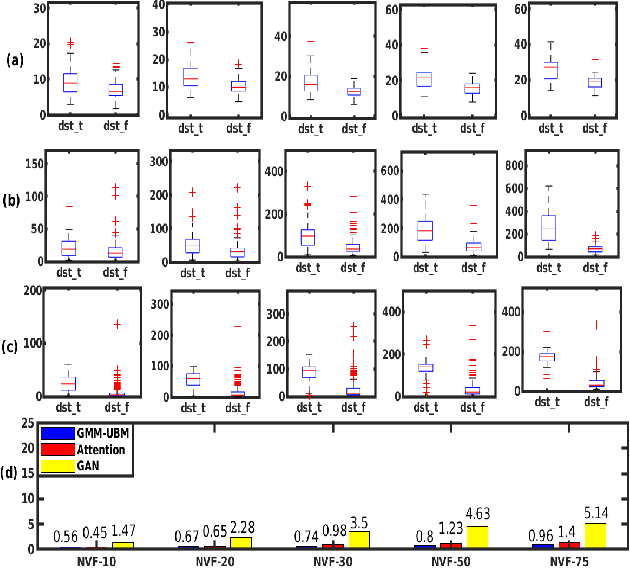
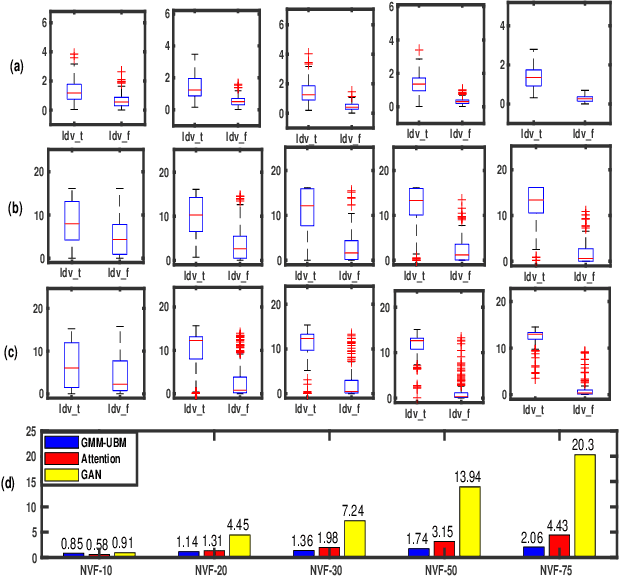
Spoken language change detection (LCD) refers to detecting language switching points in a multilingual speech signal. Speaker change detection (SCD) refers to locating the speaker change points in a multispeaker speech signal. The objective of this work is to understand the challenges in LCD task by comparing it with SCD task. Human subjective study for change detection is performed for LCD and SCD. This study demonstrates that LCD requires larger duration spectro-temporal information around the change point compared to SCD. Based on this, the work explores automatic distance based and model based LCD approaches. The model based ones include Gaussian mixture model and universal background model (GMM-UBM), attention, and Generative adversarial network (GAN) based approaches. Both the human and automatic LCD tasks infer that the performance of the LCD task improves by incorporating more and more spectro-temporal duration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge